Doors
Tuesday, January 4th, 2022

Click here to view the introduction video to explain the requirements for alterations in the ADA
Introduction:
One of the things that is confusing to some of my clients is the requirements for “alterations”. The ADA Standards for Accessible Design applies to certain types of buildings: Commercical Facilities and Public Accommodations that are built new or existing buildings, facilities or elements that are “altered”.
ADA 101.1 General. The requirements are to be applied during the design, construction, additions to, and alteration of sites, facilities, buildings, and elements to the extent required by regulations issued by Federal agencies under the Americans with Disabilities Act of 1990 (ADA).
ADA 201.1 Scope. All areas of newly designed and newly constructed buildings and facilities and altered portions of existing buildings and facilities shall comply with these requirements.
Basically, the ADA requires that not only new construction comply with the Standards, but also remodels and what they call “alteration” projects.
But what is an alteration?
The ADA defines alterations as follows:
Alteration. A change to a building or facility that affects or could affect the usability of the building or facility or portion thereof.
Alterations include, but are not limited to, remodeling, renovation, rehabilitation, reconstruction, historic restoration, resurfacing of circulation paths or vehicular ways, changes or rearrangement of the structural parts or elements, and changes or rearrangement in the plan configuration of walls and full-height partitions.
So if your project meets the definition of alteration, then it must comply with the ADA sections 202.3, 202.4 and 202.5. The newsletter will explain more in detail below.
Below are some examples of “alterations”

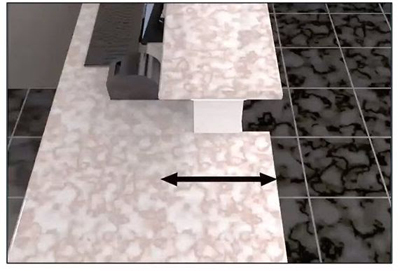
The picture above shows new flooring being installed. This is considered re-surfacing of a circulation path. This would meet the definition of alteration

The picture above shows a historic building that will be restored. This would meet the definition of alteration

The picture above shows a building that was damaged and will be re-constructed. This would meet the definition of alteration
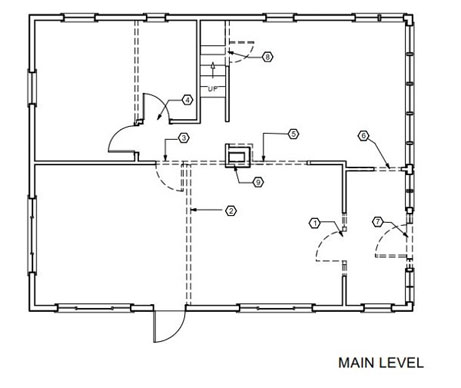
The picture above shows a demolition plan that is removing walls which will essentially reconfigures the plan. This is an alteration
The ADA also tells us what is NOT an altertion:
(from definition) the Normal maintenance, reroofing, painting or wallpapering, or changes to mechanical and electrical systems are not alterations unless they affect the usability of the building or facility.

The picture above shows a sidewalk that has broken pieces. Correcting the sidewalk would be considered maintenance and not an alteration

Not all “finishes” are exempted from having to comply. Painting vertical surfaces is an example of a project that is not an alteration.
Finishes that affect the “usability” such as flooring will trigger compliance.
What is required when the project is an alteration?
When it is determined that an “alteration” is occuring (based on the definition), then we must follow the requirements in section 202.3 which states:
202.3 Alterations. Where existing elements or spaces are altered, each altered element or space shall comply with the applicable requirements of Chapter 2.
In essense, everything new must comply with the standards. There are three exceptions: elements that are not altered (unless as noted in ADA 202.4 which we will discuss next), when it is technically infeasible (and in some jurisdictions will require a waiver or variance from the AHJ in order to make the determination) and when residential dwelling units that are not required to be accessible are altered.
EXCEPTIONS (listed in 202.3):
1. Unless required by 202.4, where elements or spaces are altered and the circulation path to the altered element or space is not altered, an accessible route shall not be required.
2. In alterations, where compliance with applicable requirements is technically infeasible, the alteration shall comply with the requirements to the maximum extent feasible
3. Residential dwelling units not required to be accessible in compliance with a standard issued pursuant to the Americans with Disabilities Act or Section 504 of the Rehabilitation Act of 1973, as amended, shall not be required to comply with 202.3.
We will focus on Exception #1 which gives us guidance if required by section 202.4. Let’s explore that section:
202.4 Alterations Affecting Primary Function Areas.
Before we delved into the additional requirements in section 202.4 it is important to understand what is considered a primary function:
Definition of Primary Function. A major activity for which the facility is intended. Areas that contain a primary function include, but are not limited to, the customer services lobby of a bank, the dining area of a cafeteria, the meeting rooms in a conference center, as well as offices and other work areas in which the activities of the public accommodation or other private entity using the facility are carried out.
Mechanical rooms, boiler rooms, supply storage rooms, employee lounges or locker rooms, janitorial closets, entrances, corridors, and restrooms are not areas containing a primary function.
A building could have many “primary functions”. In a school for example, you would have the primary function of learning, working, performing. So alterations in classrooms, as well as in the administration offices or theater will be considered alterations in areas of primary function.
A new lab counter in an existing science classroom is an alteration to an area containing a primary function
A new dining counter at an existing restaurant is an alteration of an area that contains a primary function
A new reception counter at a lobby is an alteration of an area that contains a primary function
A restroom in an office building or school is NOT a primary function space (unless it is the major activity which the building is intended, such as a rest stop, or a bathroom in a hotel guest room). Thus any alterations within the restroom is not an alteration to an area containing a primary function.
What happens when we our project affects a primary function area?
When an alteration occurrs in an area that contains a primary function, then we not only must follow the requriements of 202.3 (which state that all new elements must comply), but in addition, the path of travel elements that serve the altered area must also comply, even if they are outside the scope of the project.
202.4 Alterations affecting primary function areas. In addition to the requirements of 202.3, an alteration that affects or could affect the usability of or access to an area containing a primary function shall be made so as to ensure that, to the maximum extent feasible, the path of travel to the altered area, including the rest rooms, telephones, and drinking fountains serving the altered area, are readily accessible to and usable by individuals with disabilities, unless such alterations are disproportionate to the overall alterations in terms of cost and scope as determined under criteria established by the Attorney General. In existing transportation facilities, an area of primary function shall be as defined under regulations published by the Secretary of the Department of Transportation or the Attorney General.
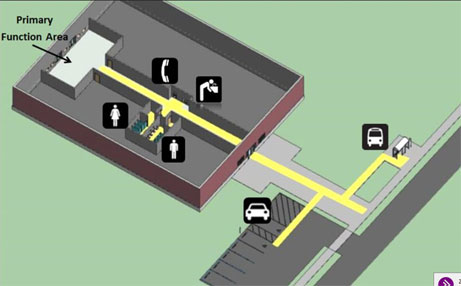
The diagram above shows the yellow line which depicts the path of travel elements leading to the “altered” area. The path of travel begins at the site arrival, then goes to the accessible entrance. It passes existing restrooms, drinking fountains and telephones that serve the altered area. All these existing path of travel elements must comply with the standards.
When a project is going to be done in an area that contains a primary function, and it is an alteration (based on the definition), the scope should include existing path of travel elements that serve the altered area IF they do not comply. There are a couple of exceptions: If the building owner (landlord) is not paying for the tenant’s improvement and if the existing conditions fall in the “Safe Harbor” clause. More on what is a safe harbor, read my newsletter on the subject.
But I am not CHANGING the function….
Many of my clients ask me that question. What if the function of the project stays the same but we are still doing a renovation of the space?
- The definition of alteration has nothing to do with “changing a function”. That terminolgoy appears in the model codes, but not in the ADA. An alteration that affects an area that contains a primary function can remain the same and still trigger compliance with 202.4 path of travel elements.
CASE STUDIES
With the above information, let’s take a look at a few examples and what it would trigger:
Case Study #1: What if we do an alteration in an existing school of an entire bathroom?
This is an existing school building where they were going to renovate the existing toilet room.
- Restrooms are not a primary function
- They are demo-ing the entire restroom
- They are installing new fixtures and new partitions.
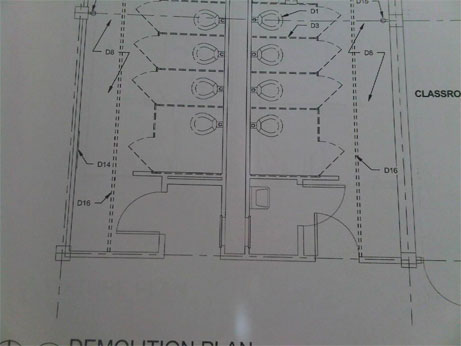
Because the toilet rooms are not a “primary function” in the school, only the new elements installed would have to comply
Case Study #2: What if we only renovate one element in the restroom?
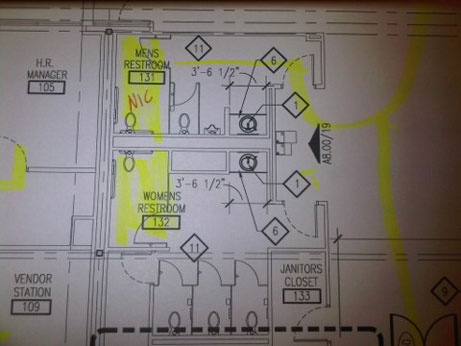
This is an existing restroom, but only the lavatory will be altered. Because the ADA allows element by element alteration, only the lavatory will have to comply. The rest of the restroom that was not altered will remain as is and will not be required to be brought up to compliance.
Case Study #3: What if only the toilet is altered?

This one is a little more complicated. Just like with the lavatory, only the toilet would have to comply. But does that mean that it would also require compliant grab bars? What about compliant toilet paper dispenser? The answer is yes. Those are also elements that are part of the water closet.
One gray area question is whether the clearance around the water closet part of the toilet?
Would the clearance need to be 60″ wide? If the
toilet room was built prior to 2012, then it is allowed to remain at 36″ clearance.
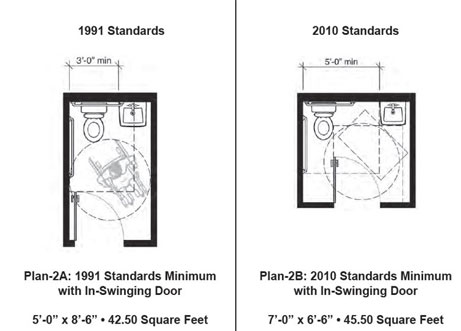
The image on the left is the 1991 ADAAG clearance at the toilet. The image on the right is the 2010 ADA Standards clearance at the toilet. If the toilet was built prior to 2012 (the year that the new standard became mandatory) then it is compliant.
Case Study #4: What if new bleachers are installed in an existing gymnasium in the school?
- The gymnasium is a primary function (it is where we learn physical education)
- The bleachers will have to comply
- The path of travel elements that serve the altered area must also comply

Case Study #5: What if we alter the floor at the gymnasium only?
- The gymnasium is a primary function
- The flooring must comply
- The path of travel elements that serve the altered area must also comply

Case Study #6 What if we paint the walls in the gymnasium only
- The gymnasium is a primary function
- Painting doesn’t affect the usability and therefore it is not an alteration

In Summary:
- Altered buildings, facilities and elements must comply
- Altered elements in an area of primary function must comply, plus:
- the Accessible entrance
- the Accessible route
- the Accessible restrooms
- the Drinking fountains
- the Telephones
- But not all of them, just the ones that serve the altered area
- Existing elements that comply with 1991 ADAAG/1994 TAS are a safe harbor
A did a presentation and attached is the .pdf for your information
Thursday, December 2nd, 2021
Sales and Service counters
Just in time for the holidays when people are shopping, this newsletter will explain what is required for people with disabilities to be able to shop and make purchases at retail stores.
The ADA Standards in section 904.4 states where provided, at least one of each type of sales counter and service counter shall comply and be accessible. Below you will see the technical requirements.
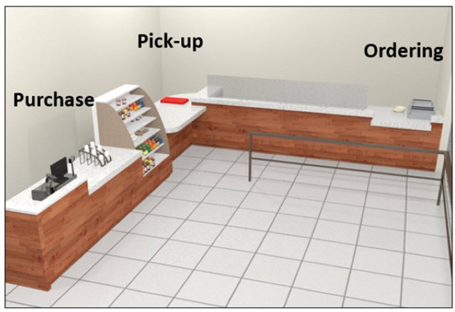
The picture above shows an “L” shape counter that has many services. Therefore each type of service will require an accessible counter.. These counters have parallel approaches.

The picture above is an information counter which is considered a “service” counter. This counter has a forward approach which is not required, but allowed. One thing to keep in mind is that no “transaction” is required for it to be considered a service counter.
Section 904.4.1 gives us the requirements that a sales or service counter must be 36” high maximum above the finished floor (it can be lower). The counter must be an integral part of the main counter. It cannot be folding, or flipping or tacked on the side of the counter.
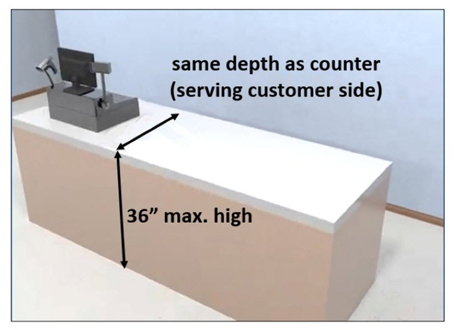
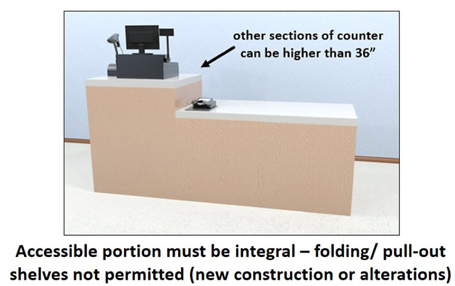
The accessible portion of the counter must be the same depth as the main (or public) side of the counter.
Even though the reception counter shown below is deeper than the public counter that is higher, the accessible portion will only have to be the same depth as the counter that is taller since that is the “public’ sales counter.
An accessible sales and service counter must be 36″ long minimum (it could be longer). Remember that the standards when they state a minimum, you are allowed to make it longer.

This counter is at the right height, but it is shorter than 36″
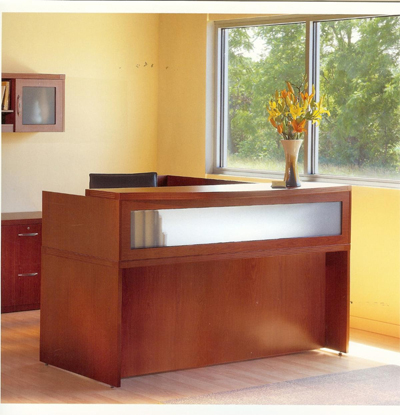

A reception that is a piece of furniture, not built in or fixed, will not have to comply with the standards, although we recommend that you provide accommodations if possible.

This accessible portion is an integral part, but a portion projects more than 4″ onto a circulation path. This was probably intended to have a forward approach knee and toe clearance (which is not required, but allowed). The counter must have cane detection on either side in order that it does not create a protruding object.
At an accessible portion of the sales and service counters, a parallel approach or a forward approach with a knee and toe clearance are allowed (depending on the preference). Either one is acceptable, but if you decide to create a forward approach, then a knee and toe clearance that complies with section 306 must be provided.

The service counter shown above has forward approach with a knee clearance

The service counter shown above has parallel approach.
Monday, November 1st, 2021
Are there any allowable tolerances in the ADA?
Construction is not a perfect science. No matter how accurate we try to draw or how careful one is to build and install materials, there will probably always be some error or omission that comes up. Best practices is to allow for the possibility of mistakes by incorporating ranges into our design. That is also what we find in the ADA and other accessibility guidelines.

How does the ADA deal with construction tolerances? First of all the tolerances ONLY apply to “construction”. There are no tolerances allowed in design. Therefore as architects and designers, we must design our spaces with enough room for construction errors. I recommend to my clients to not design to the maximums or minimums written in the Standards.
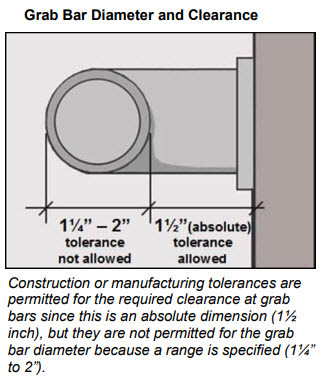
Most dimensions in the ADA Standards are specified as a minimum, maximum, or as a range. In a few areas, absolute dimensions are specified.
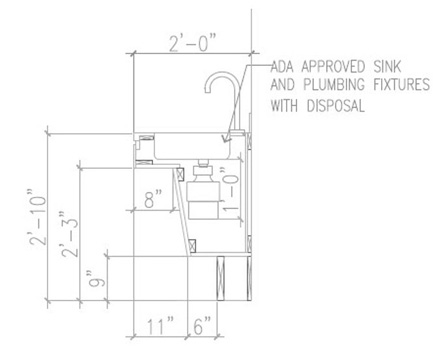
The detail shown above is showing the absolute maximums and minimum dimensions shown in the ADA Standards. There is no room for construction errors. My recommendation is to detail below the maximum and above the minimums so that you build some tolerances prior to construction.
Ranges
The 2010 ADA provides some requirements with a specified range. For example, the location of the toilet should be between 16”-18”. When a range is stated, it provides an adequate tolerance and therefore no tolerance outside of the range at either point is permitted.
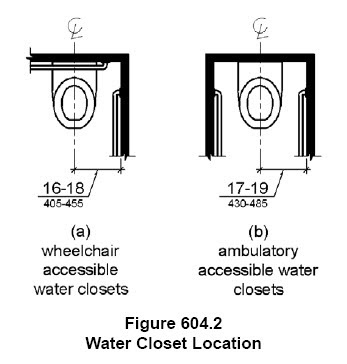
The ADA provides a range for the location of a water closet

This water closet is not compliant because it is located at 18 1/2″ from the side wall to the centerline of the toilet. Even though this water closet is located just 1/2″ beyond the allowable high range, because there was a low and high number as ranges, tolerances are not allowed. Tolerances are built in to the range.
Maximum and Minimums
When the ADA states a maximum or a minimum dimension that does not have two specific minimum and maximum end points, tolerances may apply. For example, a door pull side maneuvering clearance is stated to require 18″ min. If the door has a maneuvering clearance that exceeds the minimum allowable dimension instead, it might be allowed according to the amount of lee way given as the industry standard. According to the Access Board, only 3/32″ is allowed as tolerances for door maneuvering clearances.
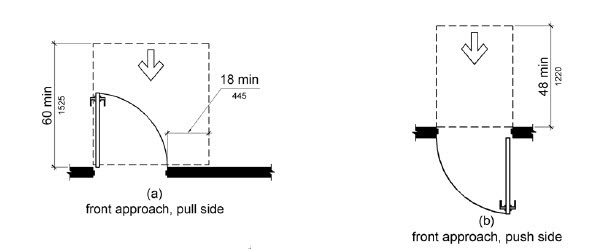
The ADA figures above show the minimum manevering clearances at the door


The door above has a maneuvering clearance of less than 18″. The clearance is 17″ clearance. Even though it is only 1″ less than what the minimum requires it does not comply with industry tolerances of 3/32″
According to the US Access Board and the Department of Justice, tolerance is an unintended, but permitted (i.e., “tolerated”), variation from a specified dimension resulting from the process of construction or manufacture. The ADA Standards recognize conventional industry tolerances for dimensions not expressed as a range. This applies to field work, not design work. Tolerances necessary for a particular manufacturing process are also permitted. Information on specific tolerances may be available from industry and trade organizations, code groups and building officials, and published references.
The position of the U. S. Access Board – as formalized in the ADA/ABA Guidelines in Section 104.1.1 – is that industry standard tolerances should be relied on when questions regarding this issue arise. However, not many trades have codified specific tolerances for many of the elements mentioned in ADA/ABA Guidelines, nor have they developed accepted industry protocols for measuring when questions of accessibility arise. Our colleagues at Corada has completed research on where to find industry standard tolerances. Here is the link
Absolute dimensions
Some dimensions in the ADA are a complete absolute. For example in a transfer shower you are only allowed a 36″x36″ size . There is no maximum or minimums allowed and there is not a range. Therefore industry standard tolerances are allowed. Some manufacturers will make the walls 36″x36″ but the base is narrower.
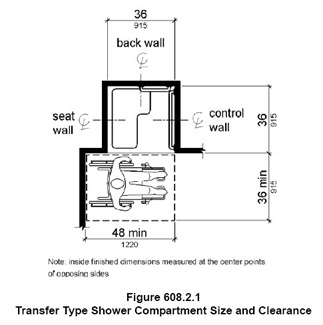

The shower above was built larger than 36″x36″

The depth of the shower was 39″

The width of the shower was 39″
Sometimes I get asked why is the transfer shower need to be exactly 36″ x36″? Below is the image of the Access Board’s reply. The shower is designed and built so that a person with disabilities can easily and safely transfer onto the shower seat and be able to reach not only the controls but the grab bars as well without much difficulty and without losing balance.

In our research we found that if the shower is constructed of gypsum board, there is a 1/8” tolerance allowed by the industry. This was found in David Kent Ballast, AIA CSI’ Handbook of Construction Tolerance page 198.
Summary
Remember that as you design, allow for construction mistakes (because we all know they happen). There are no tolerances allowances for design mistakes.
If the ADA gives you a range, don’t design to the highest or the lowest number. Always pick a number in the middle.
If the ADA gives you a number not to exceed, then there might be some tolerances, but again do not design to the maximum or minimum number they give you. Always allow for some built in tolerances.
If the ADA gives you an absolute number, then the industry standard tolerances will be able to be used if that number is not achieved. These vary but some references below have codified it.
References
National Engineering Handbook
David Kent Ballast, AIA CSI’ Handbook of Construction Tolerance
Friday, October 1st, 2021
What doors are required to comply with ADA?
There seems to be a confusion about which doors are required to comply with the Americans with Disabilities Act. Most people understand that doors that lead you to accessible public spaces and rooms have to comply. But many don’t realize that ALL doors that allows “user passage” must comply with the standards. There is just one exception: a door that allows user passage but it is leading into a room that is exempted from accessibiltiy (i.e. a machinery space).
Knowing that information, let’s delve into what doors are required to comply and what are the requirements.

Doors that allow user passage like the one shown above must comply.
Which Doors must comply?
In section 206.4 of the ADA it gives us the requirements for which type of doors must be accessible.
206.4 Entrances. Entrances shall be provided in accordance with 206.4. Entrance doors, doorways and gates shall comply with 404 and shall be on an accessible route complying with 402
206.5 Doors, Doorways, and Gates. Doors, doorways, and gates providing user passage shall be provided in accordance with 206.5.206.5.1
This paragraphs lets us know that only entrance doors are going to have requirements. Exit doors are not fully exempted. The door to “exit” a space is technically an “entrance” to the exit. Therefore the side of the door which allows user passage must also comply.

Even though this is a means of egress door and has limited requirements in the ADA Standards, it is considered a door that allows user passage and must comply.
206.5 continues to tell us which spaces must have doors that comply:
- Each entrance to a building or facility (there are some restrictions, so be sure to understand them)
- Within a building at least one door serving each room (even work areas)
- In transient lodging facilities all entrances providing user passage into and within guest rooms that ARE NOT required to provide mobility features (but only the clear width)
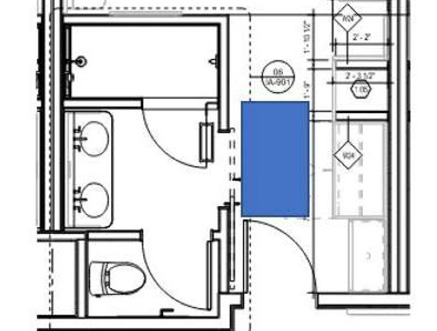
This floor plan shows a hotel room that is not required to have mobility features. All doors (except the shower door) which allows “user passage” into and within the room must comply. A 32″ clear width should be provided. All other requirements are not mandated.
A common misunderstanding is the term “user passage”. A user that they are describing is not only people who use wheelchairs, but also ambulatory and able bodied users. Therefore even if the room where the door is located is not large enought for a wheelchair, the door clear width into the room must still comply. Note the water closet room. That door must also comply with providing at least a 32″ clear width, even if the room is not large enough for a wheelchair to enter.

This storage closet appears to be the type that allows user passage, and therefore the door must comply with the techical requirements.
What are the technical requirements?
To find the technical requirements we look in section 404 which explains how to make the required doors accessible.
Doors, doorways and gates must meet the following standards:
- Must have a clear width of 32″
- Must have proper maneuvering clearances to allow for a person to open the door and go through
- The floor and ground surface at the maneuvering clearance must be stable, firm, slip resistant and must have a slope no steeper than 1:48
- A threshold that is not higher than 1/2″ must be provided
- The hardware must be the type that does not require tight grasping and twisting of the wrist, plus must be mounted between 34″-48″ a.f.f.
- The door should not close too fast (no faster than 5 seconds)
- The opening force should not be too heavy (no more than 5 lbs on an interior door)
- The bottom surface at the push side should be smooth
- If it has a vision light it should be mounted no higher than 43″ a.f.f. (a peep hole is not a vision light)
- And if there is an automatic door, there are some additional requirements (under 404.3)

This door had a clear width of 28 1/2″. The minimum requirement is 32″ clear

This picture shows the proper maneuvering clearance to reach the door handle and to go through the door

Even sliding doors are required to have maneuvering clearance. The only ones that will not is for shallow closets that do not provide user passage

This video shows you the requirements for door maneuvering clearances

The door shown above has a slope steeper than 1:48 at the maneuvering clearance, and a threshold higher than 1/2″

The door shown above has hardware that requires tight grasping and twisting of the wrist to operate
A dining counter has a forward approach knee clearance and it is 34″ a.f.f.


The door hardware in this door was mounted at 61″ a.f.f. (higher than the allowed 48″ a.f.f.)

Because the push side of the door must have a smooth surface, a foot opener cannot be used on the push side

In addition, the door hardware on the push side of the door must not be lower than 10″ a.f.f.

The vision light shown above was mounted higher than 43″ a.f.f. to the glazing.
Wednesday, September 1st, 2021
Section 810.2 Bus Loading Zones
This newsletter will speak about Bus Loading Zones both in the Public Right of Way and inside a property (like a school or other facility).

The bus stop in the above picture does not show the proper requirements for loading and unloading. This newsletter will explain why

The bus stop in the above picture is at a school and appears to have the correct area for loading children with disabilities
Technical Requirements
Bus loading zones must have an area that 96″ long measured perpendicular to the curb or vehicle roadway edge, and a clear width of 60 inches (1525 mm) minimum, measured parallel to the vehicle roadway.
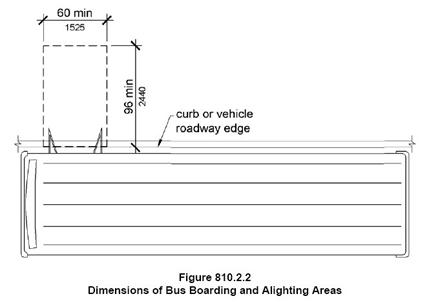

The video above shows why the 96″ long area parallel to the curb is required. The lift mechanism for a wheelchair user to enter and exit the bus requires that amount of space.
If there is a bus shelter there should be a path of travel from the bus shelter to the loading area. The path needs to be a minimum of 36″ wide. There should be an area inside the shelter that is 30″x48″ with a slope of no greater than 1:48
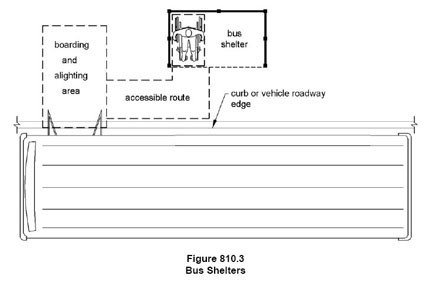
Parallel to the roadway, the slope of the bus stop boarding and aligning area shall be
the same as the roadway, to the maximum extent practicable. Perpendicular to the roadway, the slope of the bus stop boarding and alighting area shall not be steeper than1:48.
It is important to note the last requirement: The slope at a bus loading zone that is parallel with the road can be the same as the roadway and is not required to be 1:48

This bus loading zone does not have a 96″ long space parallel with the curb
Monday, August 2nd, 2021

Accessible Work Areas
Thank you to Marsha Godeaux from TDLR for taking the time to explain about employee work areas. Click here to watch the video.
This newsletter will cover Employee work areas. There is a misunderstanding that work areas are not required to comply with the ADA or TAS Standards. We will explain what is required to comply within work areas and what is exempted. Keep in mind that the requirements we are covering are only the 2010 ADA Standards and the 2012 Texas Accessibility Standards. The ABA which covers Federal Facilities do not have the same requirements.
What is a Work Area?
Employee Work Area. All or any portion of a space used only by employees and used only for work. Corridors, toilet rooms, kitchenettes and break rooms are not employee work areas.
Work Area Equipment. Any machine, instrument, engine, motor, pump, conveyor, or other apparatus used to perform work. As used in this document, this term shall apply only to equipment that is permanently installed or built-in in employee work areas. Work area equipment does not include passenger elevators and other accessible means of vertical transportation.

Work cubicles are part of a work area

a Point of Sale counter is considerd a work area as long as the public is not required to approach it.
What are the requirements?
203.9 Employee Work Areas. Spaces and elements within employee work areas shall be designed and constructed so that individuals with disabilities can approach, enter, and exit the employee work area.
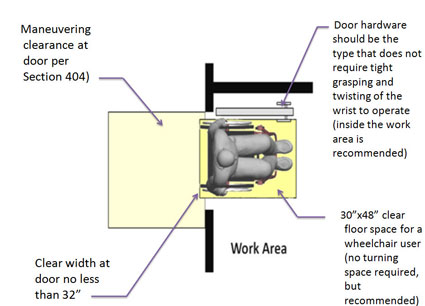
The image above summarizes the approach, enter and exist requriement

An example of a work area that only requires an approach, enter and exit would be a janitor’s closet. Elements within the janitor’s closet such as the faucet for the mop sink will not be required to comply.
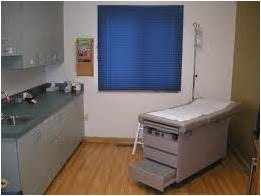
An exam room is partially a “work” area and partially a “patient” area. The area that is only used by the doctor (the sink) will be exempted from having to comply.
What are some exceptions?
Employee work areas, or portions of employee work areas, other than raised courtroom stations, that are less than 300 square feet and elevated 7 inches or more above the finish floor or ground where the elevation is essential to the function of the space shall not be required to comply with these requirements or to be on an accessible route.

This toll booth is less than 300 s.f. and elevated more than 7″ a.f.f. and therefore do not require an accessible route to it or the ability to approach it and enter it.
Common Circulation Path
In addition to approach, enter and exit, if the employee work area is larger than 1,000 s.f.. then a common path within the work area to common use spaces shall be provided
206.2.8 Employee Work Areas. Common use circulation paths within employee work areas shall comply with 402.
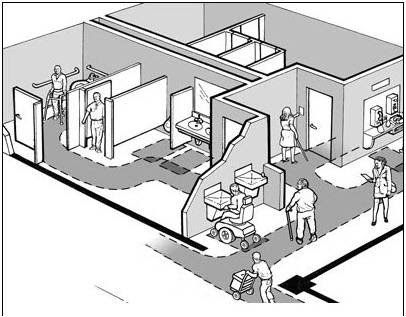
A “common” circulation path is one that is used by more than one person and not intendend for work
Section 402 states that a minimum 36″ width shall be provided along the circulation path.
EXCEPTIONS:
1. Common use circulation paths located within employee work areas that are less than 1000 square feet (93 m2) and defined by permanently installed partitions, counters, casework, or furnishings shall not be required to comply with 402.2.

This raised work area is allowed since the work area is less than 1,000 s.f.
If the path is around work area equipment, then it will not have to comply with the 36″ clear width.

This commercial kitchen has equipment that is an integral part of the work area. The 36″ min. circulation path in this space is not required to comply due to the location of the work area equipment.
Protruding Objects
Even though the only requirement for a work area is “approach, enter and exit”, it also requires that circulation path be provided. Part of the circulation path has to make sure there are no protruding objects projecting onto the circulation path more than 4″. This requirement are for any employee or visitor to the employee area that might be visually impaired.
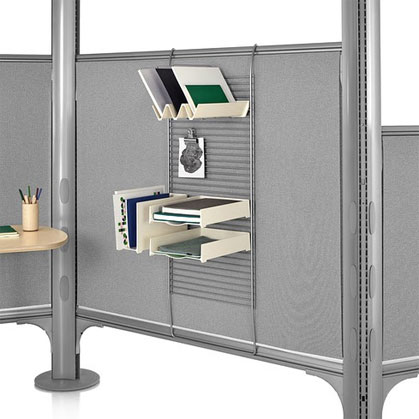

the filing system is located along the common circulation path inside the office space and projects more than 4″ onto the circulation path.
What about other employee areas that are not work related?
The requirements thus far have been for areas that are considered part of the “work” areas in a space. But there are other areas that are also part of an employee area, but are not related to the work they perform. Those areas that are NOT related to their job description will not be exempted and must comply. Below are a few examples of areas that might be for employees only, but must be fully compliant with the Standards:
Break Rooms

even though a break room is not a public area, it is still required to comply with the ADA and TAS because it is not considered a “work” area, but rather a space where they take a break from work.
LEED employee shower and employee restrooms


an employee shower or even an employee restroom are also not considered “work” areas and must comply.
Employee Locker Room

The lockers as well as the bench in this locker/dressing room must comply with the Standards
What happens when an employee is disabled?
The Standards sometimes provide additional guidance through “advisories”. These are NOT requirements, but they are suggestions that might make your design a better one. Below are some of the advisories on work areas:
Advisory 203.9 Employee Work Areas. Although areas used exclusively by employees for work are not required to be fully accessible, consider designing such areas to include non-required turning spaces, and provide accessible elements whenever possible.
Under the Title I of the ADA, employees with disabilities are entitled to reasonable accommodations in the workplace; accommodations can include alterations to spaces within the facility. Designing employee work areas to be more accessible at the outset will avoid more costly retrofits when current employees become temporarily or permanently disabled, or when new employees with disabilities are hired.

Thursday, July 1st, 2021

Abadi Accessibility is proud to support the Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA) 31st Anniversary. On July 26th we celebrate this important civil rights law that works to ensure all people with disabilities have the same rights and opportunities as everyone else. Celebrate with us by visiting: www.adaanniversary.org/ #ADA31 #ThanksToTheADA
How are you planning to celebrate Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA) 31st Anniversary? This July 26th the ADA National Network and individuals, communities, and organizations across the country will be participating. Learn how you can be involved by visiting www.adaanniversary.org/ #ADA31 #ThanksToTheADA
Introduction to our newsletter:

After I wrote my first newsletter about counters, my clients are still not clear on all the different requirements for the different types of counters and fixed or built-in surfaces that the ADA requires to be accessible. First of all let me review that there are five type of counters scoped in the ADA Standards: Work surfaces, dining counters, service counters, sales counters and check out counters. Then there are two type of counters that are not scoped: work area counters and non-work area common use counters that do not fall under the other listed. There are also Food service lines, as well as other portions public side service areas. For those please check out my newsletter I wrote I 2014.
This newsletter will explain the different requirements for dining surfaces, non-employee work surfaces and sales and service counters.
Dining Counters
According to Scoping section 226, at least 5% of seating spaces and standing spaces at dining surfaces must comply with 902. Standing spaces are those counters where people might stand to eat or drink rather than sit. Those counters must also comply. Some examples of dining counters are bars where drinks are served, fast food establishments with fixed tables, and booths and banquettes at a restaurant.

These fixed dining counters in a cafeteria is an example of a dining surface.

a bar is an example of a dining surface
Section 902 gives us direction on how to make the dining surfaces accessible:
- There must be a knee clearance complying with section 306 so that a person in a wheelchair will approach and use the counter in a forward approach
- The height of the counter must be between 28″-34″ a.f.f. PLEASE NOTE….WE RECOMMEND TO NEVER USE THE MINIMUMS OR MAXIMUMS WHEN DESIGNING.
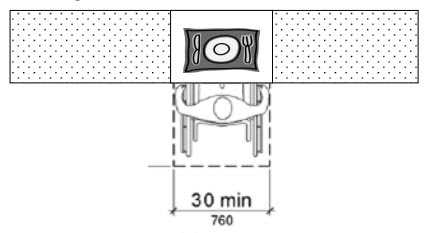
A dining counter should have a 30″ width and a 17″ min. depth at the knee clearance.

A dining counter has a forward approach knee clearance and it is 34″ a.f.f.

This is a dining counter but also a service window. It is acceptable to have the dining counter in front of the service counter
Non-Employee Work Surfaces
Section 226 tells you that 5% of non-employee work surfaces must comply and meet the requirements set forth in section 902. These are also required to be dispersed throughout the space they are in. Section 902 states that a work surface must have a forward approach with a knee space per section 306 and be 30″ wide minimum and 34″ high maximum

Study carrols in a library is an example of a non-employee work surface

Diaper changing counters are also considered a “work surface”

A patient registration desk is another example of a non-employee work surface
All the requirements in section 902 are for non-employee work surfaces (or for the public). Employee work surfaces that are part of a work area are exempted until such time when a person with disabilities is hired at which point, the surface must be provided to accommodate them and their abilities.
Sales and Service counters
Where provided, at least one of each type of sales counter and service counter shall comply with 904.4.
Where counters are dispersed throughout the building or facility, counters complying with 904.4 also shall be dispersed.
Keep in mind that the requirements are the either sales or service counters. The term “transaction” is no longer used. A transaction could occur but it is not the only pre-requisite for compliance.
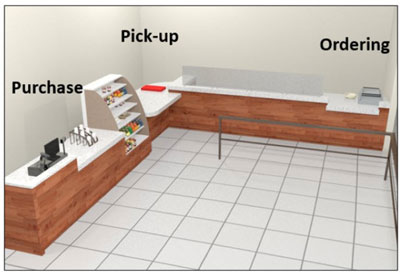
The counter shown above has different functions (some are sales and some are service). Each one must have a portion at an accessible height
Section 904 gives us the following requirements for sales and service counters:
- 36” high maximum
- Same depth as the main counter
- 36” length min.
- Parallel approach OR Forward approach allowed
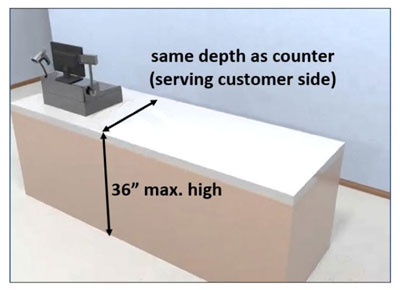
the accessible couter must be 36″ a.f.f. maximum and at least 36″ long

A sales or service counter can have either with a forward approach knee clearance or a parallel or side approach.

The accessible portion of the counter must be the same depth as the main (or public) side of the counter. Even though the reception counter is deeper than the public counter, the accessible portion will only have to be 36″ a.f.f. maximun and 36″ min. long the same depth as the public counter (which can be higher than 36″ a.f.f.)

The reception desk is considered a “service” counter because information is a service a business would provide to their guests. The one shown above did not have a 36″ long counter

A service or sales counter may not be the type that is flipped up, or pushed in once it is used. it must be a permanent counter that is always available.
Monday, August 3rd, 2020
Introduction
The ADA Standards (and the Texas Accessibility Standards) states:
106.5.5 Alteration. A change to a building or facility that affects or could affect the usability of the building or facility or portion thereof. Alterations include, but are not limited to, remodeling, renovation, rehabilitation, reconstruction, historic restoration, resurfacing of circulation paths or vehicular ways, changes or rearrangement of the structural parts or elements, and changes or rearrangement in the plan configuration of walls and full-height partitions.
Normal maintenance, reroofing, painting or wallpapering, or changes to mechanical and electrical systems are not alterations unless they affect the usability of the building or facility.
|
|
When doing “alterations” in buildings you have two sets of requirements: Requirements for alterations ( ADA Section 202.3) and requirements for alterations that occur in an area that contains a primary function ( ADA Section 202.4) If your alteration is in an area that is not a primary function, only the new things will have to comply. Some examples are doing renovation in bathrooms, break rooms, closets etc.
If your alterations are in an area that is considered primary function then all the new things must comply, but also the path of travel elements that serve the altered area including: accessible route, entrance, restrooms, drinking fountains and telephones that serve the altered area. In Texas they included parking that serves the altered area.
|
|
The yellow line in the figure above depicts the path of travel elements that must be compliant when an alteration occurs in an area that contains a primary function
|
|
Case studies
With the above information, let’s take a look at a few examples and what it would trigger:
Case Study #1: What if we do an alteration in an existing school of an entire bathroom?
|
|
This is an existing school building where they were going to renovate the existing toilet room.
- Restrooms are not a primary function
- They are demo-ing the entire restroom
- They are installing new fixtures and new partitions.
|
|
Because the toilet rooms are not a “primary function” in the school, only the new elements installed would have to comply
|
|
Case Study #2: What if we only renovate one element in the restroom?
|
|
This is an existing restroom, but only the lavatory will be altered. Because the ADA allows element by element alteration, only the lavatory will have to comply. The rest of the restroom that was not altered will remain as is and will not be required to be brought up to compliance.
|
|
Case Study #3: What if only the toilet is altered?
|
|
This one is a little more complicated. Just like with the lavatory, only the toilet would have to comply. But does that mean that it would also require compliant grab bars? What about compliant toilet paper dispenser? The answer is yes. Those are also elements that are part of the water closet.
One gray area question is whether the clearance around the water closet part of the toilet? Would the clearance need to be 60″ wide? If the toilet room was built prior to 2012, then it is allowed to remain at 36″ clearance.
|
|
The image on the left is the 1991 ADAAG clearance at the toilet. The image on the right is the 2010 ADA Standards clearance at the toilet. If the toilet was built prior to 2012 (the year that the new standard became mandatory) then it is compliant.
|
|
Case Study #4: What if new bleachers are installed in an existing gymnasium in the school?
- The gymnasium is a primary function
- The bleachers will have to comply
- The path of travel elements that serve the altered area must also comply
|
|
Case Study #5: What if we alter the floor at the gymnasium only?
- The gymnasium is a primary function
- The flooring must comply
- The path of travel elements that serve the altered area must also comply
|
|
Case Study #6
What if we paint the walls in the gymnasium only
- The gymnasium is a primary function
- Painting doesn’t affect the usability and therefore it is not an alteration
|
|
-
In Summary:
•Existing buildings are not “grandfathered”. They must comply
•Texas requires compliance at the time of construction
•ADA requires compliance when it is readily achievable
•Existing buildings that comply with 1991 ADAAG/1994 TAS are a safe harbor
•Altered elements must comply
•Altered elements in an area of primary function must comply, plus:
•Accessible entrance
•Accessible route
•Accessible restrooms
•Drinking fountains
•Telephones
•Parking
Here is a presentation I did about the subject
|
|
Friday, January 3rd, 2020
As most of us know, the minimum clear widths along an accessible route that the ADA requires are 36″ minimum clear. But there are times when are allowed to be narrower or required to be wider. This newsletter will explain those instances.
|
Clear Width Reduction
In the 2010 ADA guidelines, section 403 gives us a figure to follow which explains that the 36″ wide clear width can be reduced to 32″ clear as long as the distance that you travel through the narrower width is no more than 24″ deep.
403.5.1 Clear Width. Except as provided in 403.5.2 and 403.5.3, the clear width of walking surfaces shall be 36 inches (915 mm) minimum.
EXCEPTION: The clear width shall be permitted to be reduced to 32 inches (815 mm) minimum for a length of 24 inches (610 mm) maximum provided that reduced width segments are separated by segments that are 48 inches (1220 mm) long minimum and 36 inches (915 mm) wide minimum.
But do both sides of the path need to be 24″ long the way it is shown in the figure above? Could one side be a wall or even a longer cabinet or obstruction? I was inspecting a restroom and found that condition. There was a cased opening to enter the toilet compartment area. One side of the cased opening was 8″ deep and the other side was the restroom wall which was longer than 24″.
|
|
| This is the photo of the cased opening along the route to the sinks |
|
|
| This is the plan of the cased opening (where it says “Align”) which part of it is 8″ on one side and longer than 24″ on the other side. The opening was less than 36″ wide. |
The guidelines allow this. As long as one side of the path is no more than 24″ long and it goes back to 36″ wide, it will be an acceptable condition.
|
Clear width at the approach to a toilet compartment
A clear path to a toilet compartment (both wheelchair and ambulatory) should also have a 36″ minimum clear width. Except that at the approach to the door it must increase to 42″ in width
604.8.1.2 Doors. Toilet compartment doors, including door hardware, shall comply with 404 except that if the approach is to the latch side of the compartment door, clearance between the door side of the compartment and any obstruction shall be 42 inches (1065 mm) minimum
The standard is giving us requirements for the door clearance only. The path to the toilet compartment is still required to have a 36″ minimum clear width. But the space to open the toilet compartment door and the maneuvering clearance (if the approach is on the latch side) must have a 42″ minimum clear width between the door and the obstruction
|
|
This photo shows the plan view of a path to the ambulatory toilet compartment.
|
In the plan view above you can see a furred out column in front of the toilet compartments. That fur out is located within the door maneuvering clearance of the ambulatory toilet compartment and it reduces the 42″ required width to 36″
This figure above shows the door maneuvering clearance at the latch side approach. A toilet compartment door will only require 42″ of clear width not 48″ like a standard door.
|
Passing space
Along an accessible route you are required to have 36″ clear width. This width is required to be widened to 60″ every 200 feet. This is to allow people in wheelchairs and pedestrians to pass each other.
403.5.3 Passing Spaces. An accessible route with a clear width less than 60 inches (1525 mm) shall provide passing spaces at intervals of 200 feet (61 m) maximum. Passing spaces shall be either: a space 60 inches (1525 mm) minimum by 60 inches (1525 mm) minimum; or, an intersection of two walking surfaces providing a T-shaped space complying with 304.3.2 where the base and arms of the T-shaped space extend 48 inches (1220 mm) minimum beyond the intersection
Here is a video from the Access Board that explains it
|
Clear width at turns
When a wheelchair makes a ninety degree turn, a 36″ minimum clear width is allowed.
But when a wheelchair is required to make a 180 degree turn, like in a narrow corridor, or maybe in a queue line or library stacks, then the width will have to increase from 36″ to 42″ depending on what size the element they are turning around is.
403.5.2 Clear Width at Turn. Where the accessible route makes a 180 degree turn around an element which is less than 48 inches (1220 mm) wide, clear width shall be 42 inches (1065 mm) minimum approaching the turn, 48 inches (1220 mm) minimum at the turn and 42 inches (1065 mm) minimum leaving the turn.
EXCEPTION: Where the clear width at the turn is 60 inches (1525 mm) minimum compliance with 403.5.2 shall not be required.
For instance if the space that they are turning around is 60″ in depth, then the clear width can be 36″ min. If the space is 48″, then the clear width will have to increase to 42″
This video will give you some guidance on turning and wheelchair clearances
|

Wednesday, August 1st, 2018
|
In order for a person with disabilities to enter a building on their own, there needs to be enough room for them to get through the door and into the spaces. This newsletter will explain what the requirements are for doors so that a person can easily open the door and go through it.
What types of doors need to comply?
In the 2010 ADA standards for accessible design the only doors that require compliance with doors that people will pass through:
ADA Section 404.2 Manual Doors, Doorways, and Manual Gates. Manual doors and doorways and manual gates intended for user passage shall comply with 404.2.
That means that if a door is located in a shallow closet, for example, that door is not technically intended for a person to pass through and therefore it does not have to comply
|
|
Why do we need so much room in front of the door?
The amount of maneuvering clearances at the door depends on the approach to the door. Section 404 shows you the different ways that a person could approach the door and gives you guidance for the amount of clearance a person will need to reach for the door handle, open the door and go through.
The most well-known requirements are the forward approach pull and push.
But why do we need so much room? The rectangle shown in the figure provides the proper amount of space for a person with disabilities to reach the door handle, open the door and go through. Below are four images depicting the amount of space required for a forward approach pull side maneuvering of the door.
Interestingly enough, a door might be located in a thicker wall, or an object might be located on the same wall as the maneuvering clearance. As long as the object is no more than 8” deep, or as long as the door is not located more than 8” from the face of the wall, it will be compliant for maneuvering for forward approach pull or push side. Below are some examples:
 This door is located in a recess that is less than 8” deep. The 18” on the pull side maneuvering can include the wall that is in front of the door.  This door has a paper towel dispenser next to the 18” maneuvering clearance at the latch side of the door  Since the paper towel dispenser is less than 8” deep, it can be part of the maneuvering clearance
But there are other ways one can approach the door, and the requirements for the amount of maneuvering clearance will change. The table in section 404 shows the different approaches and the amount of space required for each. The US Access Board created instructional videos to explain the standards. Here is the one about maneuvering clearances |
|
Other types of doors
The requirements for doors also applies to toilet compartment doors. Except for the latch side approach which requires only 42″ of clearance, all other approaches will require the space per section 404
The requirements so far dealt with swinging doors and gates. But besides the swing doors, there are also maneuvering requirements for sliding doors. These also require maneuvering and these are found in section 404.
|
|
| this is a barn door that will require maneuvering clearance to open |
|
|









 Abadi
Abadi 
























































































































