Doors
Monday, June 3rd, 2024
Accessible Signage Location
The 2010 ADA (and other States standards like Texas) section 216 requires that signage that designates interior rooms that are permanent (which means that their function will not change in the future due to the fixtures within). Those signs must have raised characters and braille. Although pictograms and symbols are not required, if they are provided, they must also comply with the standards.
Some of the requirements are for height and location of signs. This newsletter will focus on that requirement and will provide examples of some problematic rules.

Height of the sign
The 2010 ADA states that the signs required to comply must have raised characters and there should be brailled that matches the words of the raised characters and located directly below the corresponding words.
703.2 Raised Characters. Raised characters shall comply with 703.2 and shall be duplicated in braille complying with 703.3.
The height of the sign is in relationship to the raised characters. In other words, the Standards require that the bottom of the raised characters be located between 48″-60″ a.f.f.
703.4.1 Height Above Finish Floor or Ground. Tactile characters on signs shall be located 48 inches (1220 mm) minimum above the finish floor or ground surface, measured from the baseline of the lowest tactile character and 60 inches (1525 mm) maximum above the finish floor or ground surface, measured from the baseline of the highest tactile character.


Door Signage that has both name of room and room numbers must also meet the requirements. The bottom most baseline of the raised characters should not be mounted lower than 48″ a.f.f. and the top most baseline should not be mounted higher than 60″ a.f.f.

The sign is mounted higher than 60″ a.f.f. to the baseline of the raised characters
Where should the sign be located?
Signs have requirements on where they need to be located.
1. If it is provided at a door, they must be mounted alongside the door at the latch side. Although they are allowed to be located on the push side of doors with closers.

The sign must be located adjacent the latch side of the door. If there is a sign on the door, it can stay there as long as there is also a second sign where it is required

The sign should not be located on the door on the pull side of the door because if a person is reading it, the door could open and hit them
2. Where a tactile sign is provided at double doors with one active leaf, the sign shall be located on the inactive leaf.
3.. Where a tactile sign is provided at double doors with two active leafs, the sign shall be located to the right of the right hand door.

4..Where there is no wall space at the latch side of a single door or at the right side of double doors, signs shall be located on the nearest adjacent wall.


Sign located at the wall adjacent the latch/handle of the door

The wall beyond the swing of the door is less than 18″ and therefore the sign did not have the centerline at 9″ at the floor space beyond the arc.

The sign can be mounted to a glass wall if it is adjacent the latch side of the door
5..Signs containing tactile characters shall be located so that a clear floor space of 18 inches (455 mm) minimum by 18 inches (455 mm) minimum, centered on the tactile characters, is provided beyond the arc of any door swing between the closed position and 45 degree open position.

The ADA figure shows the 18″x18′ clear floor space at the sign. It must be centered at the sign and also located beyond the arc of the door.

The clear floor space of 18″x18″ was obstructed by a drinking fountain

The clear floor space at the sign was obstructed by a drinking fountain.
Wednesday, January 3rd, 2024

BECAUSE IT WAS A PROTRUDING OBJECT
What is a protruding object?
Most of the rules in the 2010 ADA Standards for Accessible design seems to be relating to people who use wheelchairs. But the guidelines apply to other disabilities besides mobility. There are guidelines to assist person who are hearing impaired, congnitively impaired as well as visually impaired.
People who are visually impaired use the built environment to find the way. They might use a cane to “feel” objects which will guide them and will assist them to avoid any hazards. People who use a cane can only detect objects that are located along their circulation path and mounted BELOW 27″ a.f.f.
A circulation path is not the same as an accessible route.
When you see the words “accessible route” in the ADA Standards it is describing the path a person in a wheelchair would use to get around. When you see the words “circulation path” in the ADA Standards it describes any path that a pedestrian would take regardless of disability. Most of the time, the circulation path applies to persons that are visually impaired.

People who are visually impaired use the built environment to find the way. They might use a cane to “feel” objects which will guide them and will assist them to avoid any hazards. People who use a cane can only detect objects that are located along their circulation path and mounted BELOW 27″ a.f.f.
Anything that is mounted ABOVE 27″ a.f.f. or below 80″ a.f.f. could be considered a protruding object IF it is more than 4″ from the mounting surface.
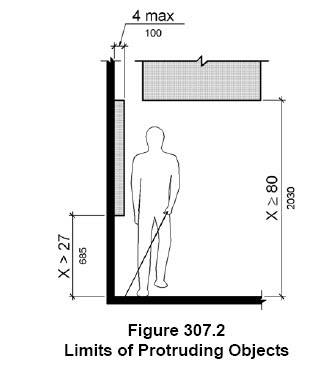
But are any object that extends more than 4″ from its mounting surface a “protruding object”?
No….only if they are also located in a circulation path.
A circulation path in the ADA is not the same as what we design professionals think of a circulation path. We think of it ONLY as corridors, walkway, elevators, stairs….
A circulation path in the ADA describes ANY place that a able bodied pedestrian will be going. This would include the path you would take to go from the doorway to the toilet inside a restroom, the path from the toilet to the sink inside a restroom, the path from a doorway to your seat in a conference room or classroom, the path from one room to a different room etc.
“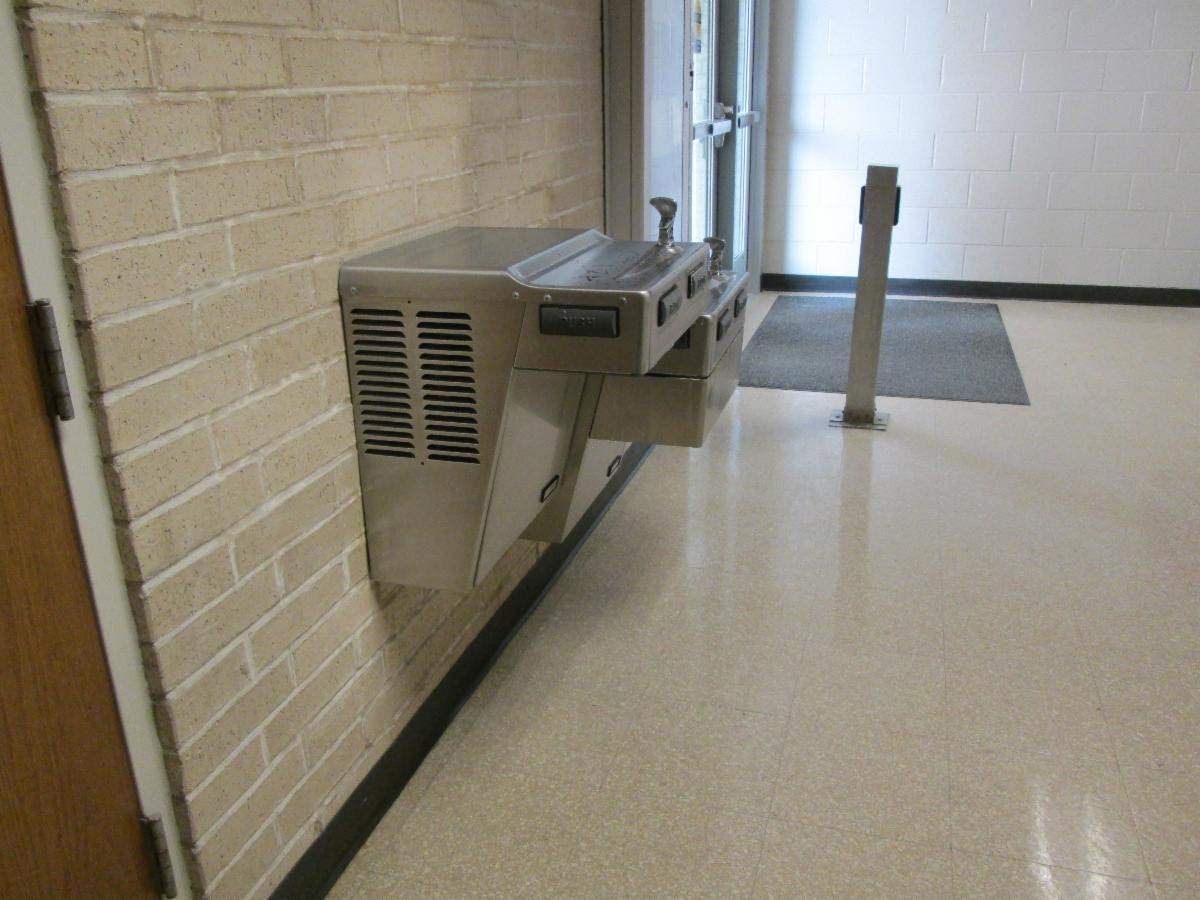
The photo above is showing a drinking fountain in a circulation path from one room to another
Some people ask me, but there is plenty of room in the middle of the corridor where the drinking fountain does not protrude…..Yes, but a person who is visually impaired who uses a cane to find their way is trained to walk close to the walls in order that they can tap the cane on a surface which will gude them to where they are going. So the middle of the corridor would not be THEIR circulation path.

The photo above is showing a diaper counter located in the circulation path to the toilet compartments as well as the exit door. It also projects more than 4″ onto that circulation path making it a protruding object.
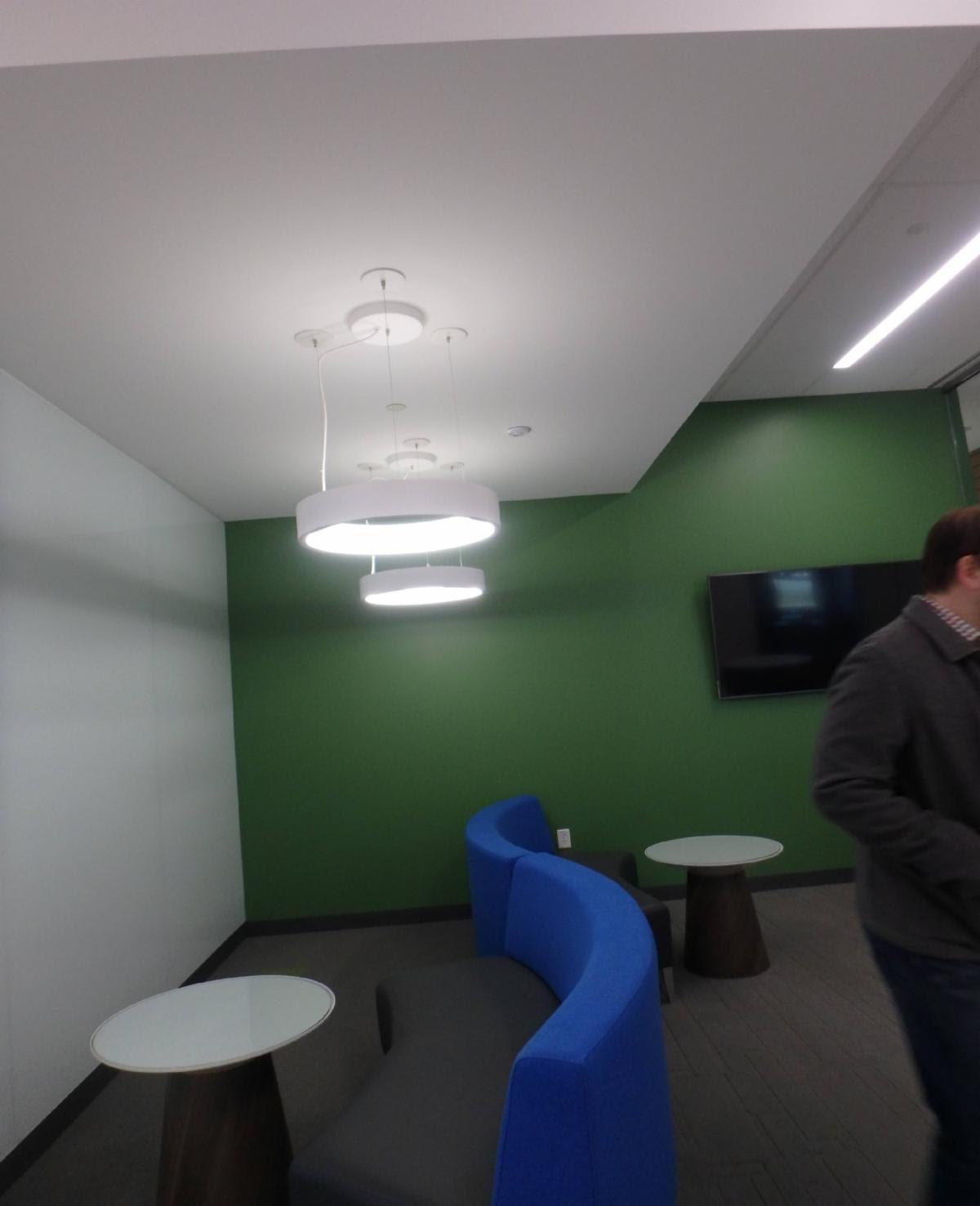

The photo above is showing a pendant light fixture mounted lower than 80″ a.f.f. and in a circulation path from one side of the room to the other. But you might say that there is a seat located right below it. Unless that seat is FIXED or BUILT IN it does not constitute a cane detectable element because it could be moved from that location. Only permanent elements will be able to be used as cane detection.
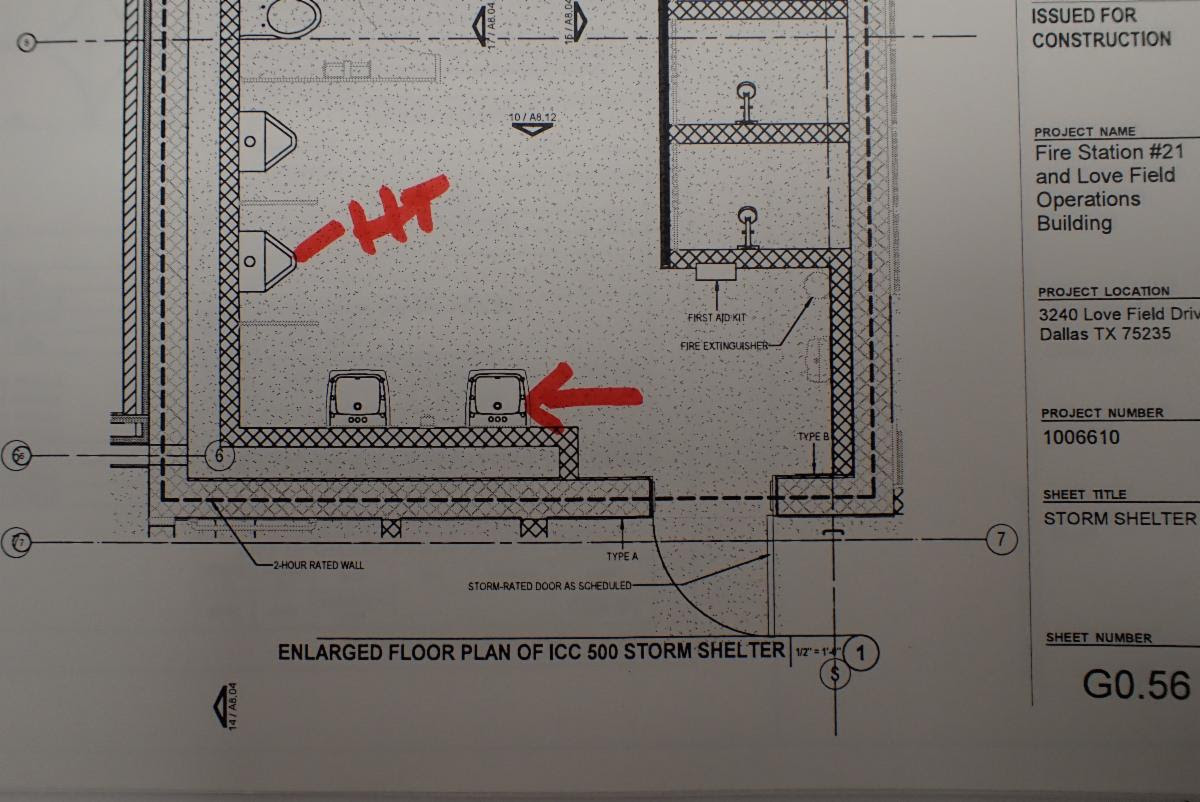
The drawing above is showing a plan of a lavatory located on the way to the urinals and showers at this lavatory might be a protruding object if the leading edge is mounted higher than 27″ a.f.f. which is possible since the knee space for a lavatory is required to be a minimum of 27″ a.f.f.
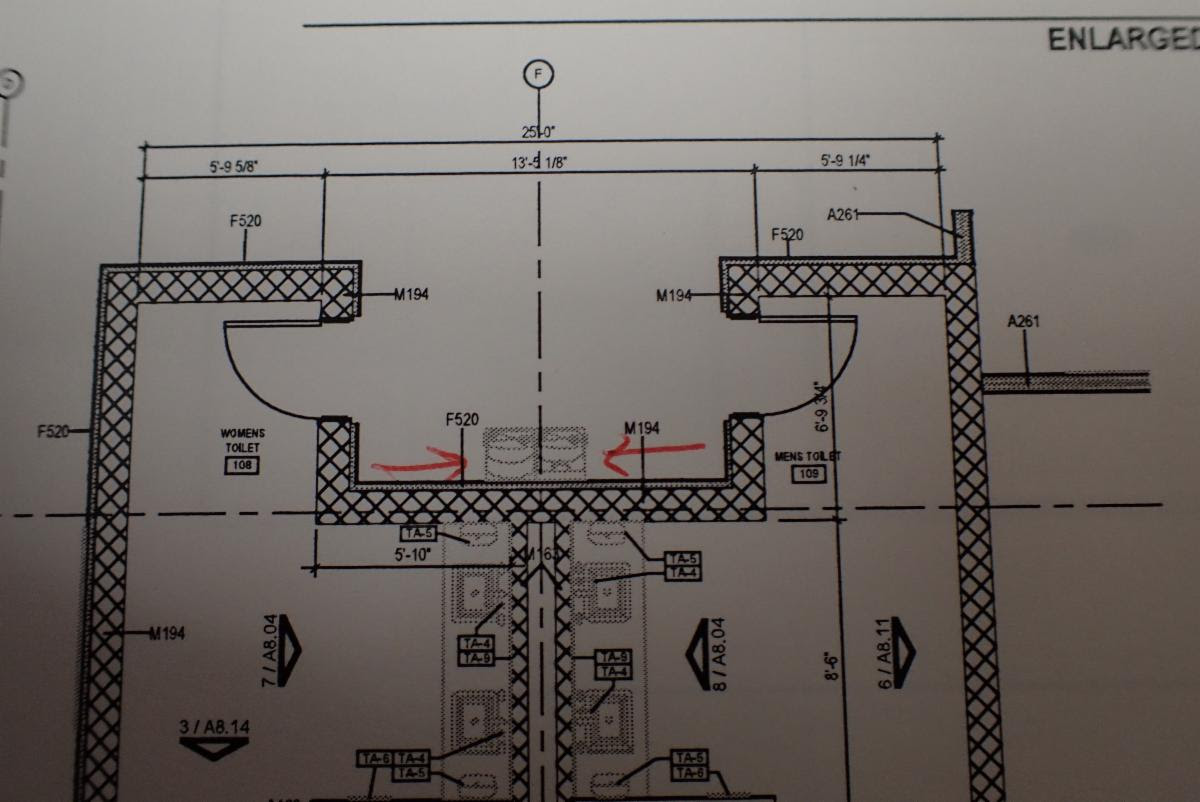
The floor plan above is showing a set of drinking fountains in an alcove. It appears as though the alcove puts them away from the circulation path, but because the alcove is wide a person who is visually impaired could accidentally walk into the drinking fountain if one of the leading edges are higher than 27″ a.f.f.
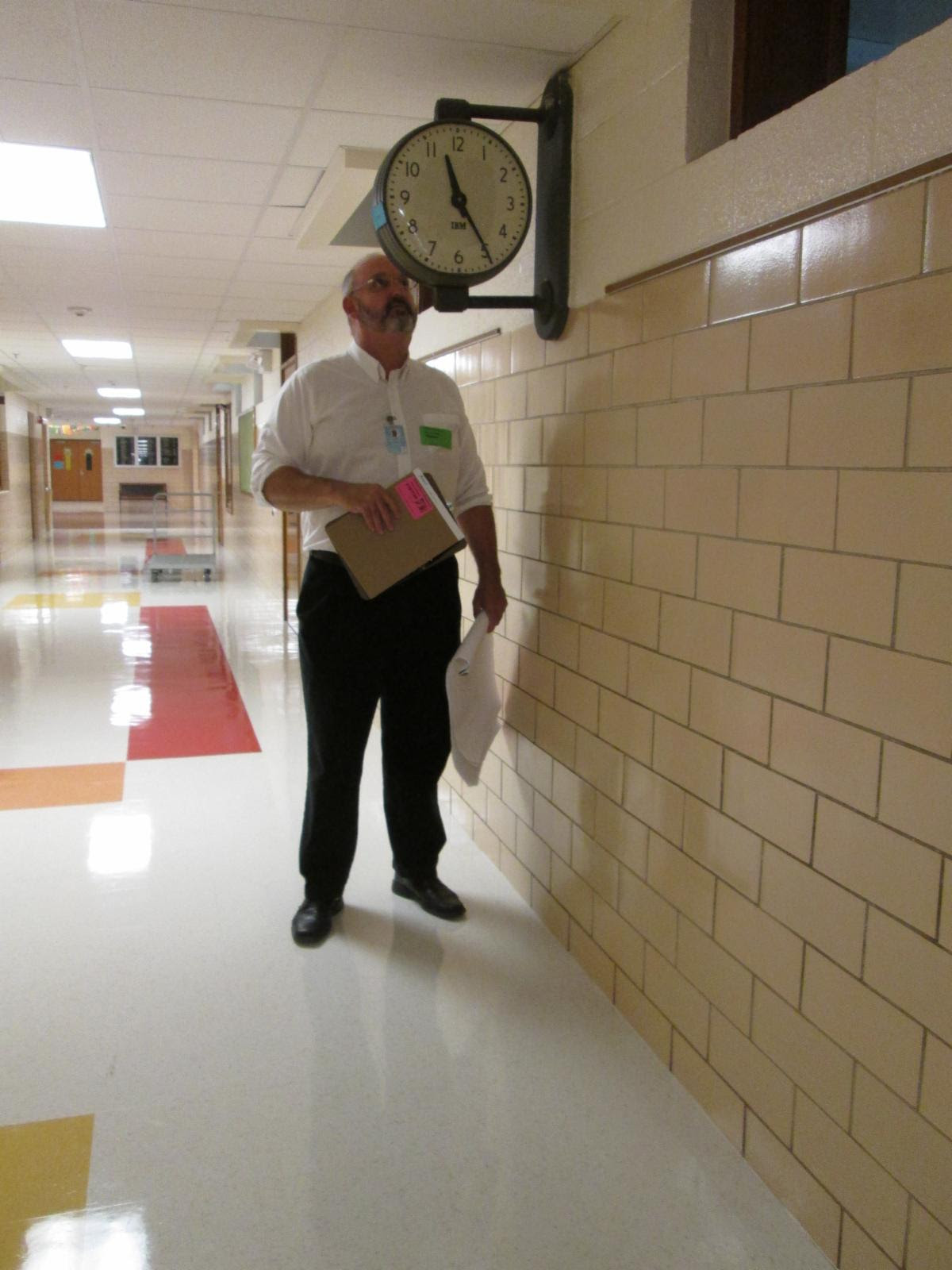

The photo above is showing a clock mounted on a wall in a corridor of a school and lower than 80″ a.f.f.. The clock is a hazard to people who are visually impaired because it protrudes more than 4″ onto the circulation path.
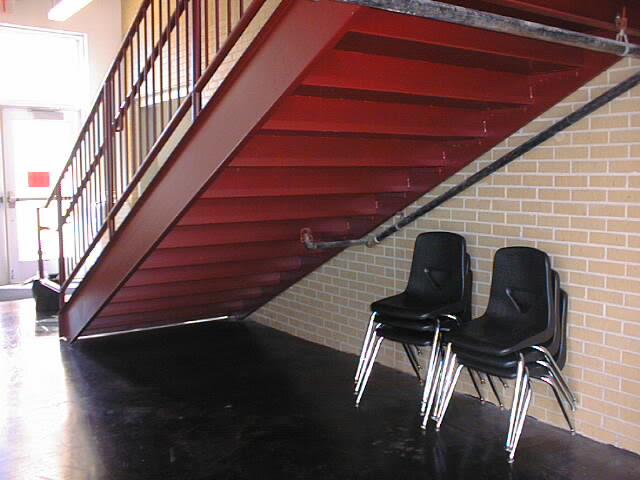

The photo above is showing stair with exposed risers and treads. There is no cane detection and a person who is visually impaired could bump their head on the edges.
There are some requirements that sometimes get mistaken for protruding objects. For example, there is a rule that forbids certain objects to overlap the clearance of the toilet in a restroom. Designers might think that the rule pertains to protruding objects and as long as the object within the clearance of the toilet is less than 4″ it is allowed to overlap.
That is not correct.. The protuding object rule, remember, has to do with persons who are visually impaired. The requirement at the toilet has to do with persons in wheelchairs where such objects would prevent them from easily transfer onto the water closet.
“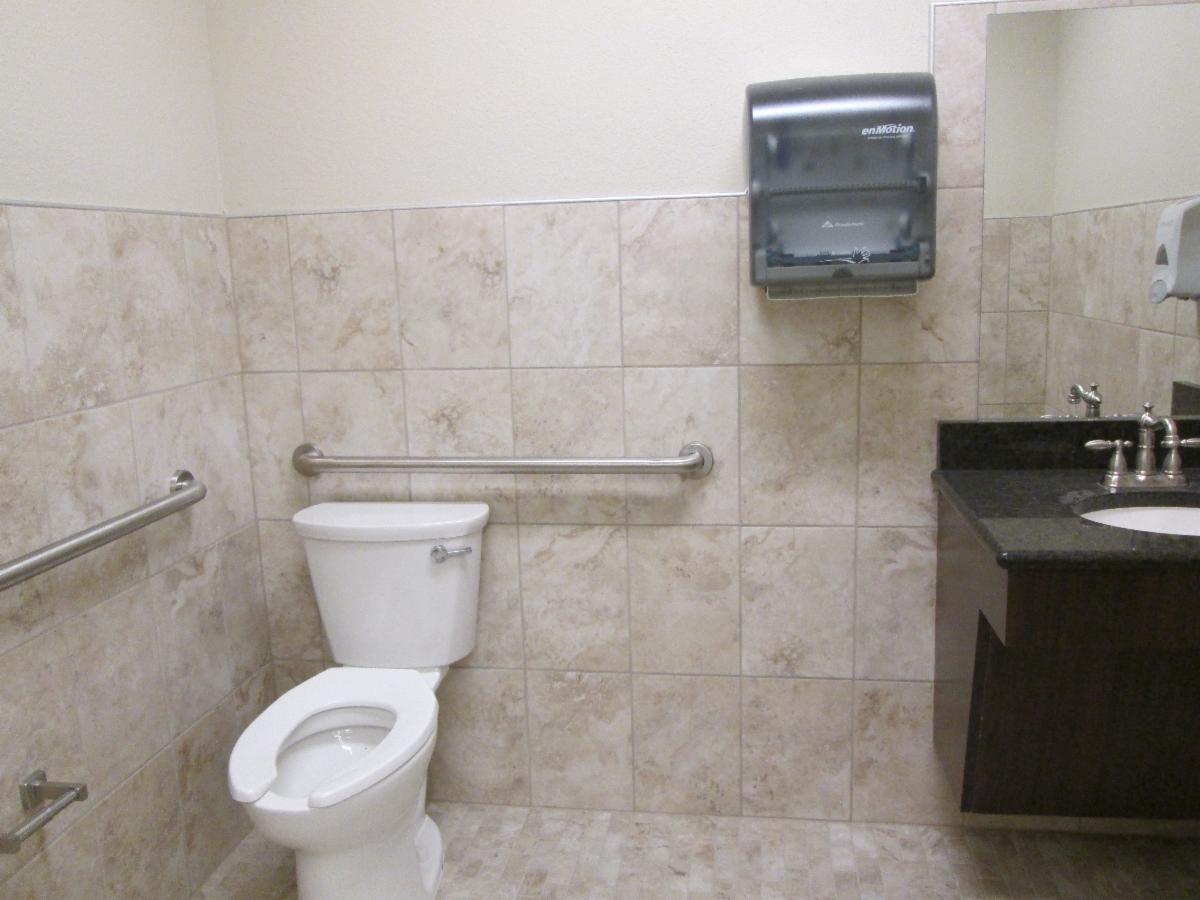
The photo above is showing a paper towel dispenser that is overlapping the clearance around the toilet. This is NOT a protruding object because it is not lcoated in a circulation path. The paper towel dispenser is located between the toilet and the lavatory which both act as cane detection away from the paper towel dispenser. This however is a violation of the overlap rule for toilets (ADA section 604.3.2)
Some Solutions
Below are some solutions to resolve the protruding objects.
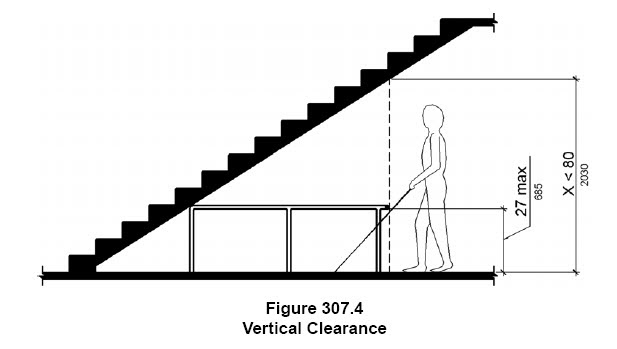
The figure above shows a way to provide cane detection by using a rail below an open stair
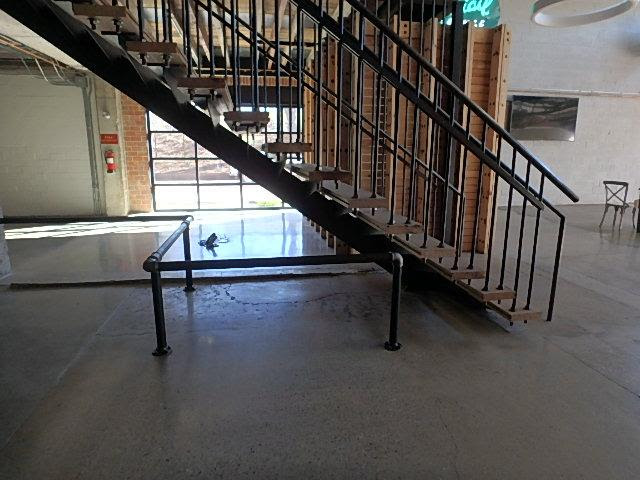

The photo above shows a rail below an open stair that acts as cane detection
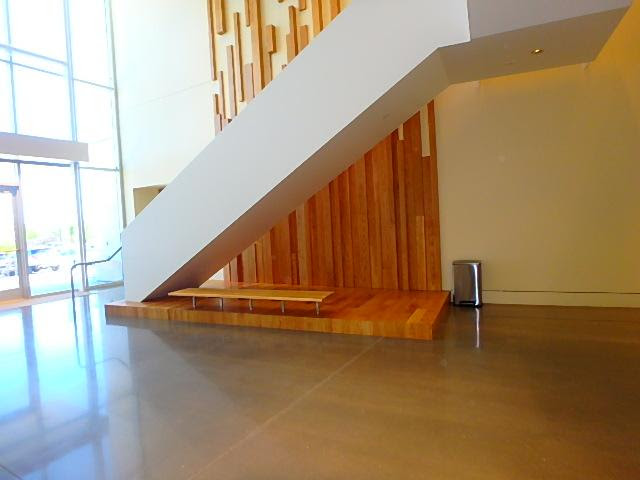

The figure above shows a way to provide cane detection by using a rail below an open stair
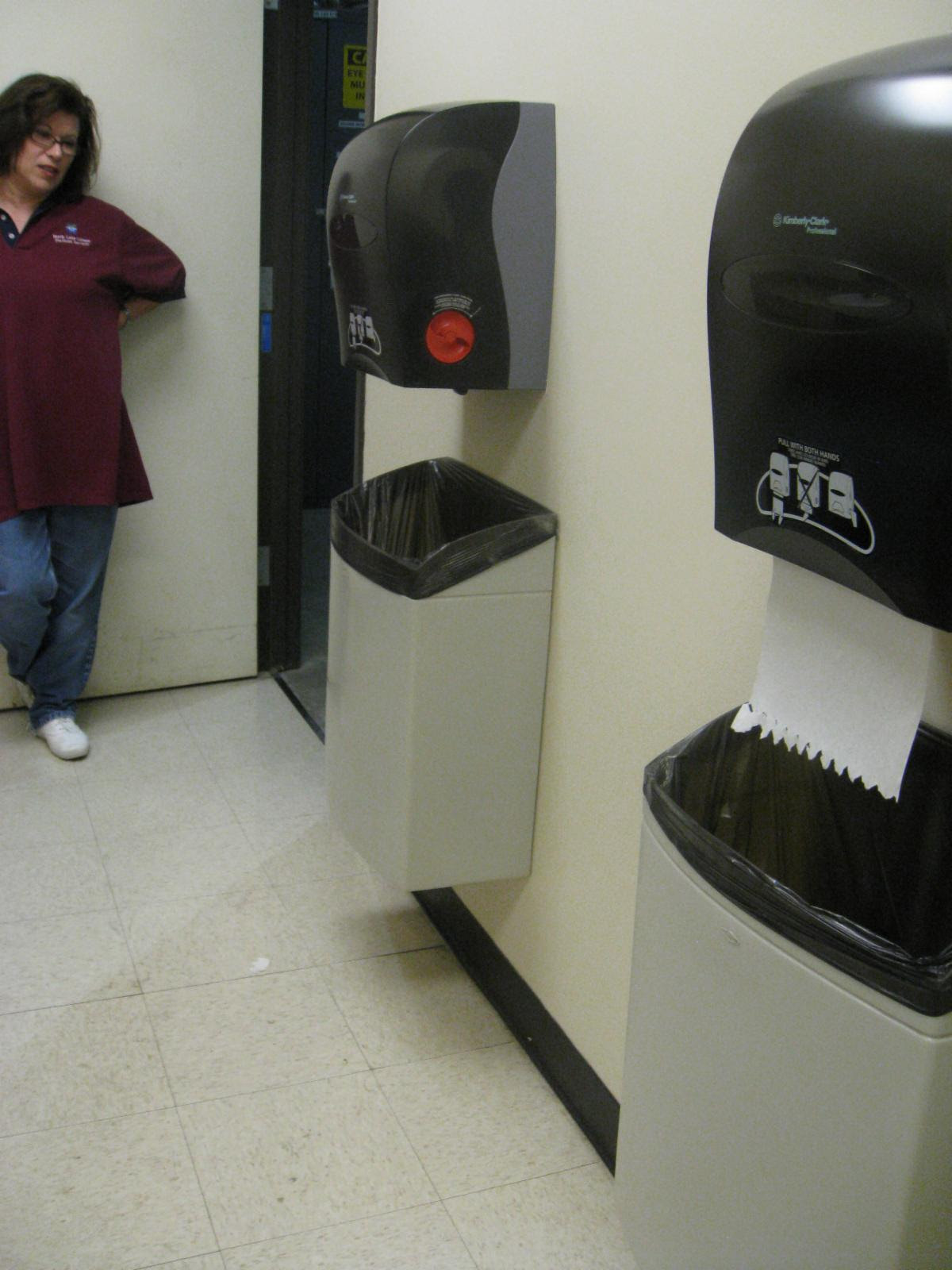

The photo above trash receptable mounted below the paper towel dispensers that are protruding more than 4″ onto a circulation path inside the restroom. This trash receptible reaches below 27″ a.f.f. which makes it cane detectable.

The photo above shows a cane detectable apron that is an accessory you can specify to be installed below the leading edge of the high drinking fountain. The cane detectable apron should be mounted exactly at 27″ a.f.f. so that it acts as cane detection and allows the wheelchair drinking fountain to have the required knee clearance.
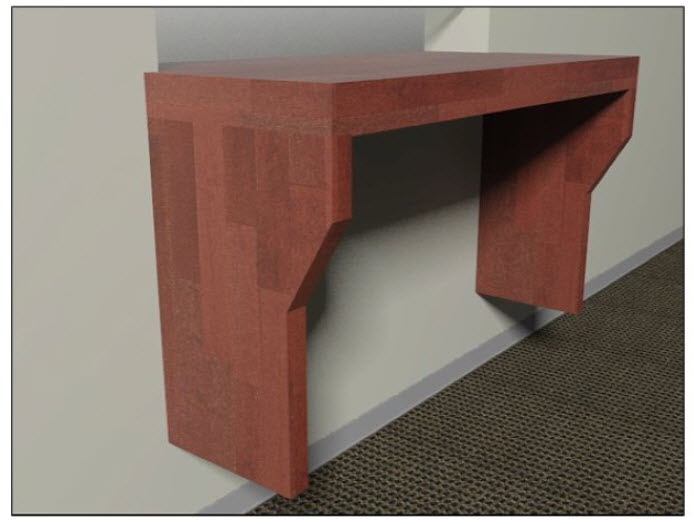

The photo above shows panels on either side of a wall mounted counter which acts as cane detection
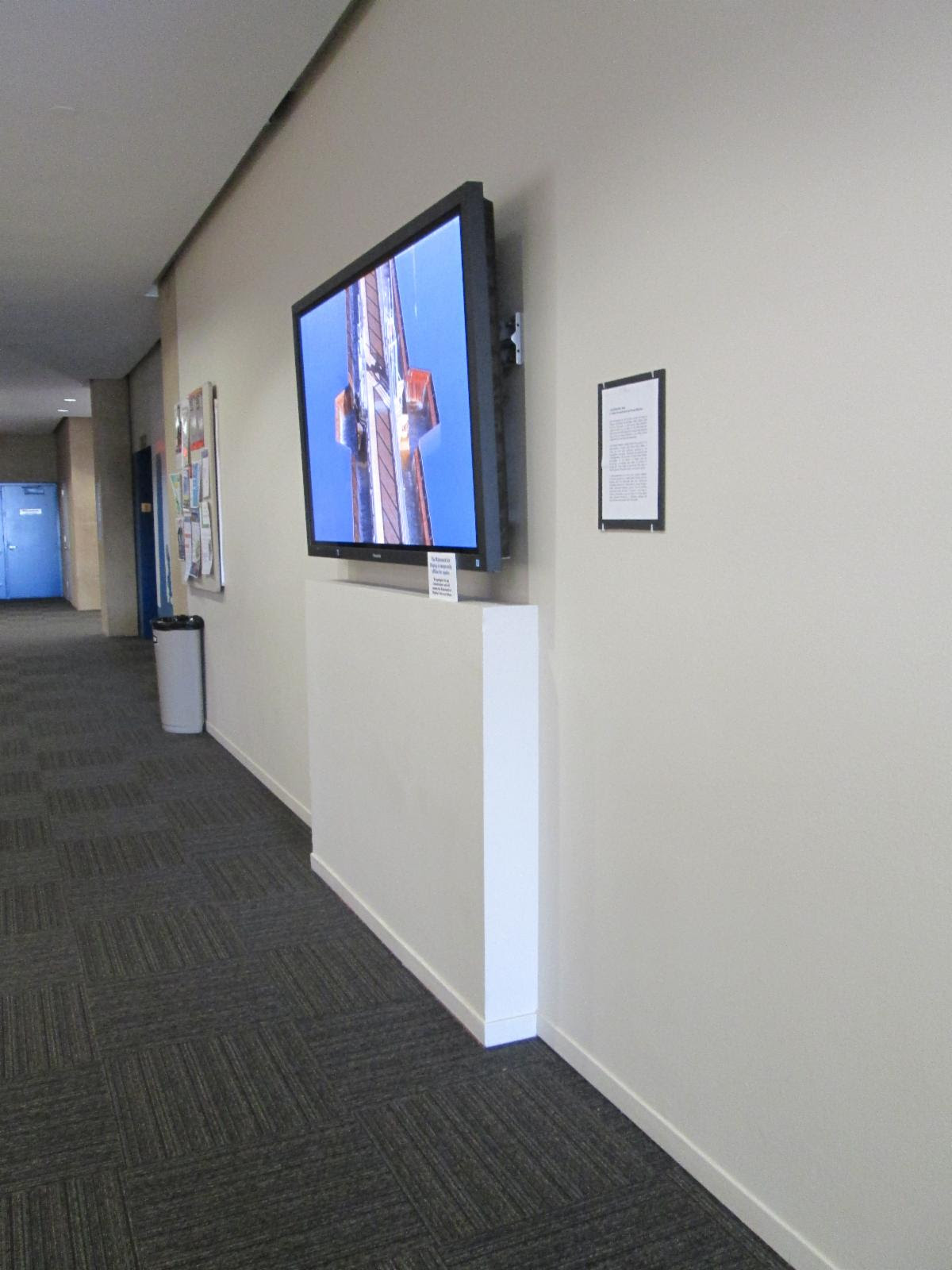

The photo above shows a furred out wall that acts as cane detection to the wall mounted TV located in a circulation path.
Friday, December 1st, 2023
This newsletter will be discussing the requirements for the 2010 ADA Standards for Accessible Design as well as the 2012 Texas Accessibility Standards. Other Standards and Codes might have different requirements
Accessible Means of Egress
Every once in a while I receive a phone call asking me about accessible exits. They wonder about the location of the exit, whether the door needs to be accessible, about stairs, stoops etc. My answer always confuses them:

In section 207 of The 2010 ADA and 2012 TAS have the following requirements:
- Means of Egress shall comply with section 1003.2.13 of the IBC (2000 edition and 2001 supplement) or
- Means of egress shall comply with section 1007 of the IBC 2003 edition
That means that The ADA and TAS DO NOT have jurisdiction over the requirements for accessible means of egress. Only the AHJ will have oversight over the number and location of the accessible means of egress.
TAS and ADA do focus on entrances. So if an exit door is also an entrance then it would have to comply (if it is a required accessible entrance). The door, shown in the photo below, does not have door hardware to enter, so this would be a purely a means of egress and would not be required to comply on the exterior. There might be requirements depending on where it is located to be accessible on the interior if it was considered an entrance to the exterior (you would be “entering” the exterior)
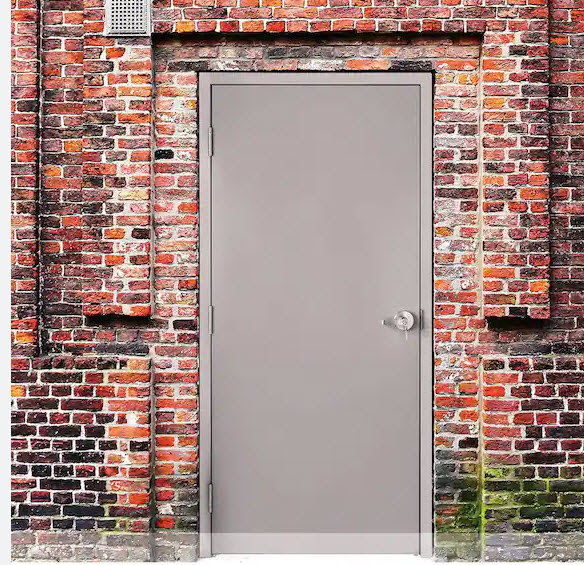


The photo shown above is an exit door that has hardware on the exterior. If this door is also an entrance then it will have to comply
Section 207 of the ADA and TAS has two exceptions that might not be the same as the IBC:
- The accessible means of egress can share the common path of egress if permitted by local building or life safety codes
- Areas of refuge shall not be required in detention and correctional facilities.
There is an advisory, not required but advisable that the ADA and TAS also have regarding the accessible means of egress:
Advisory 105.2.4 ICC/IBC.
International Building Code (IBC)-2000 (including 2001 Supplement to the International Codes) and IBC-2003 are referenced for means of egress, areas of refuge, and railings provided on fishing piers and platforms.
At least one accessible means of egress is required for every accessible space and at least two accessible means of egress are required where more than one means of egress is required.
The technical criteria for accessible means of egress allow the use of exit stairways and evacuation elevators when provided in conjunction with horizontal exits or areas of refuge. While typical elevators are not designed to be used during an emergency evacuation, evacuation elevators are designed with standby power and other features according to the elevator safety standard and can be used for the evacuation of individuals with disabilities.
The IBC also provides requirements for areas of refuge, which are fire-rated spaces on levels above or below the exit discharge levels where people unable to use stairs can go to register a call for assistance and wait for evacuation.
Signage at the accessible means of egress is also required by ADA and TAS. Those rules will not be covered in this newsletter, but can be found in section 216.4
“
Friday, September 1st, 2023
Recessed Fixtures adjacent to water closets
In the ADA Standards, Texas Accessibility Standards and ICC ANSI A117.1 the rear wall grab bar is required to be a minimum 36″. There is an exception to be able to use a shorter when the water closet is located on the same wall as a recessed plumbing fixture.
604.5.2 Rear Wall. The rear wall grab bar shall be 36 inches (915 mm) long minimum and extend from the centerline of the water closet 12 inches (305 mm) minimum on one side and 24 inches (610 mm) minimum on the other side.
EXCEPTIONS:
1. The rear grab bar shall be permitted to be 24 inches (610 mm) long minimum, centered on the water closet, where wall space does not permit a length of 36 inches (915 mm) minimum due to the location of a recessed fixture adjacent to the water closet.
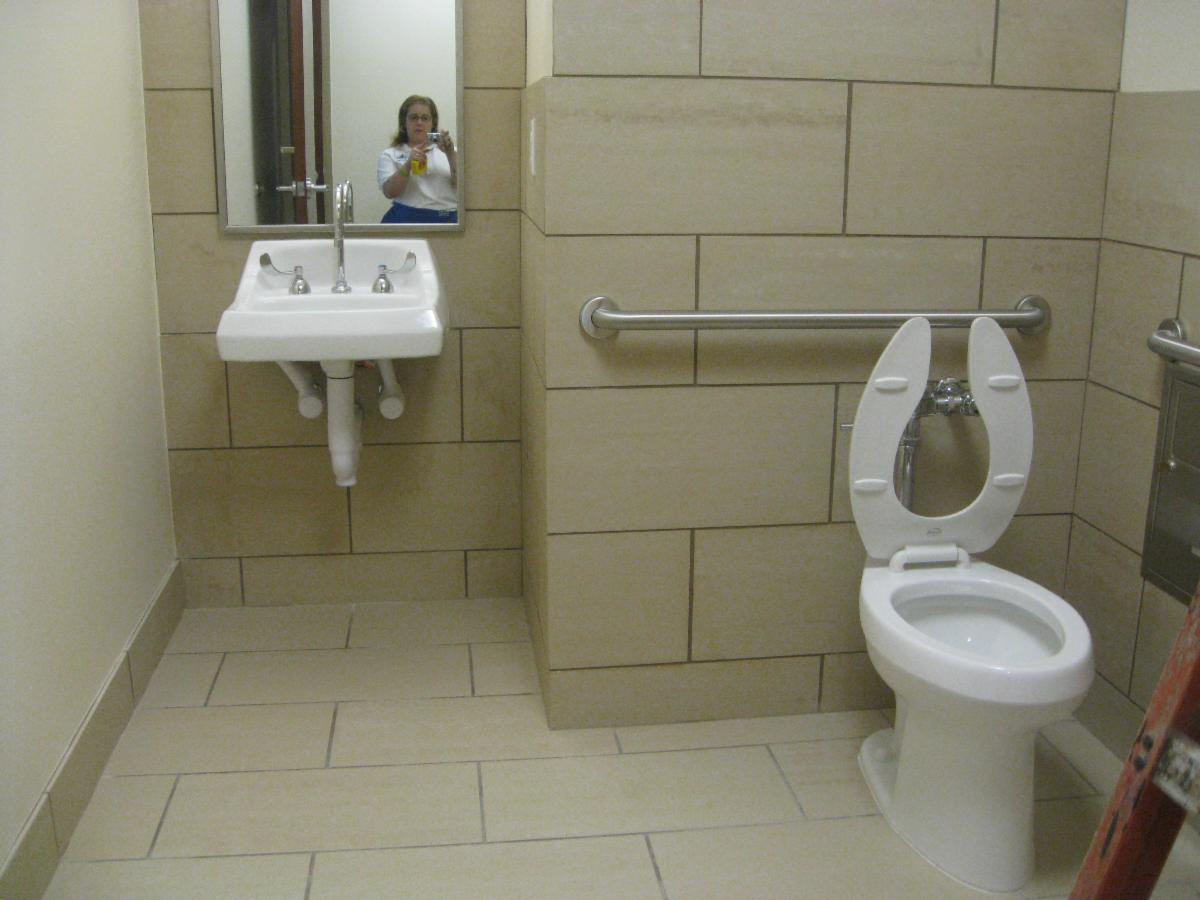

This is recessed lavatory adjacent to the the water closet
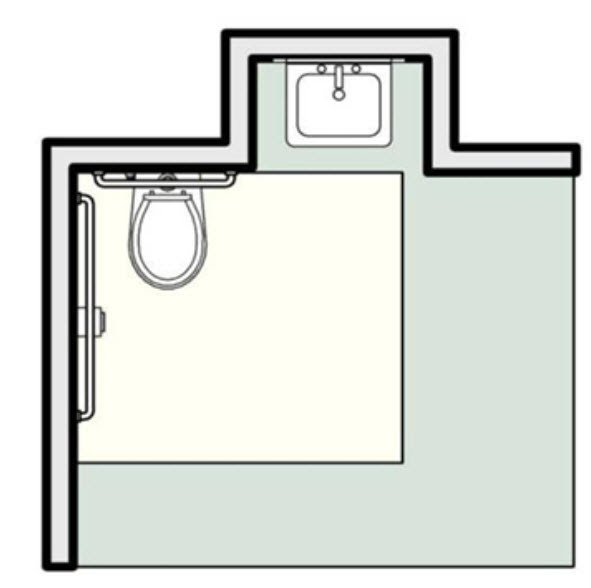
This is a plan view of the recessed lavatory adjacent to the water closet which creates the wall condition too short to install a 36″ grab bar. This condition is allowed to have a 24″ rear wall grab bar installed centered on the toilet.
But is a lavatory the only fixture allowed to be recessed adjacent to the toilet? No. Actually any fixture that is recessed will allow the rear wall grab bar to be shorter. A shower that is recessed and adjacent to the toilet will also allow the exception to be taken
This is a plan view of the recessed shower adjacent to the water closet which creates the wall condition too short to install a 36″ grab bar. This condition is also allowed to have a 24″ rear wall grab bar installed centered on the toilet.
Recessed Doors
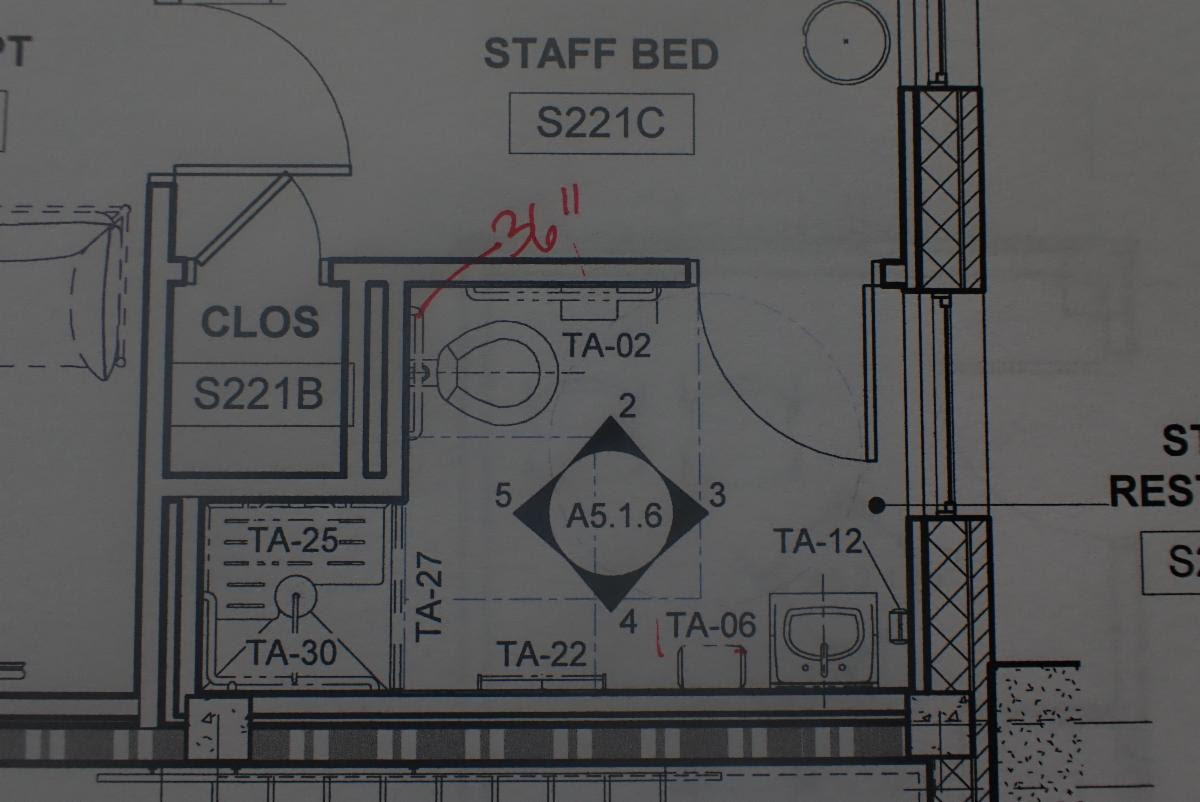
A door that is located within a wall that is no thicker than 8″ measured from its face to the front of the wall will be considered a “recessed” door. Also if there is an object located next to the door latch and it is not 8″ perpendicular from the face of the door to the front of the object, it will also be considered a “recessed” door.
404.2.4.3 Recessed Doors and Gates. Maneuvering clearances for forward approach shall be provided when any obstruction within 18 inches (455 mm) of the latch side of a doorway projects more than 8 inches (205 mm) beyond the face of the door, measured perpendicular to the face of the door or gate.
“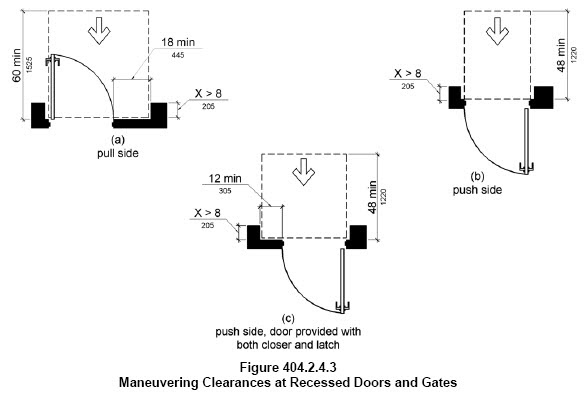
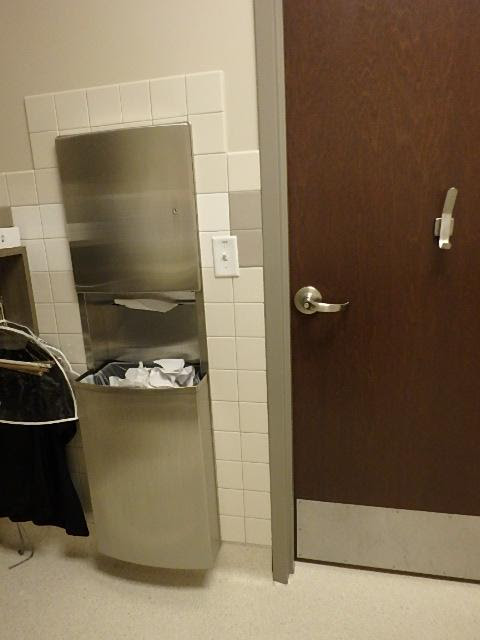


The door shown above has a trash receptacle within the maneuvering clearance. Since the trash receptable is less than 8″ it is allowed to be included in the manuevering clearance to reach the door handle
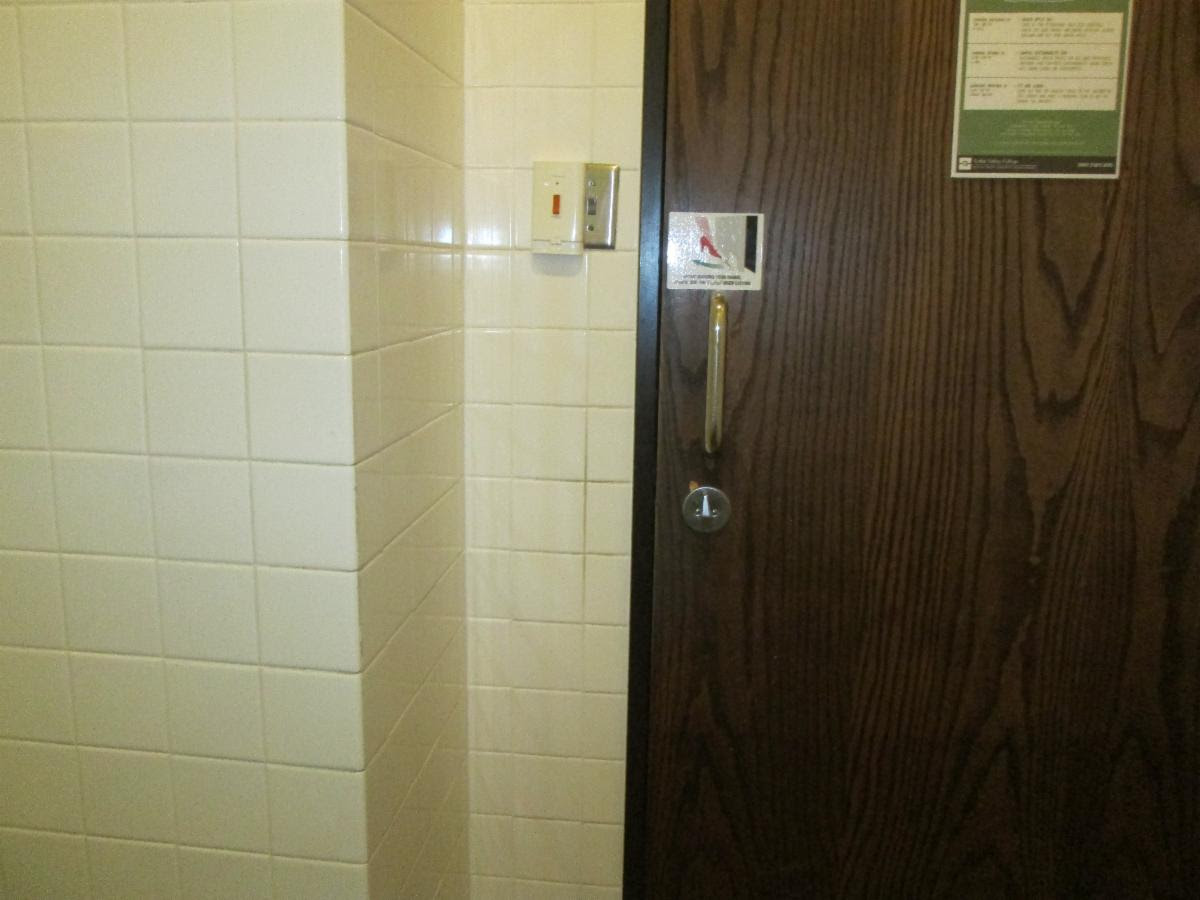

The door shown above is located in a small alcove that is 8″ deep. The maneuvering clearance will be acceptable for a “recessed” door.
Recessed elements in Alcoves
A clear floor space for wheelchairs is required to be a minimum of 30″ x 48″. But if an element is located in an alcove that is more than 24″ deep, then the clear floor space will need to increase to 36″ wide for a forward approach or 60″ long for a side approach.
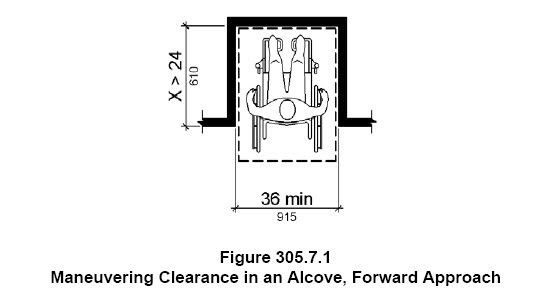
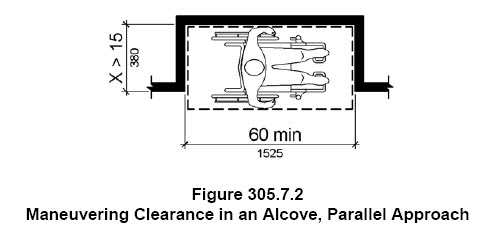 .
.
The drinking fountain shown above is an alcove and therefore the clear floor space must be 36″ min. wide
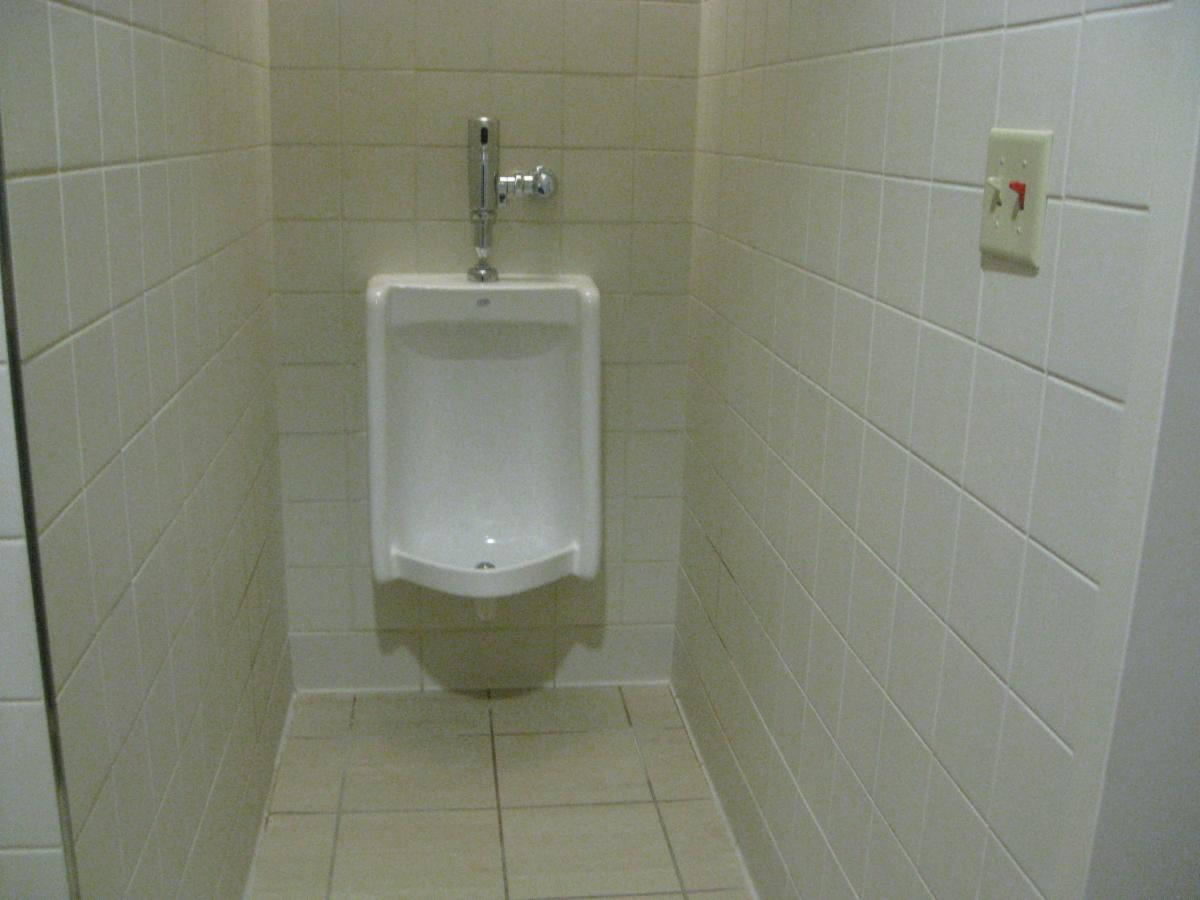

The urinal shown above is an alcove and therefore the clear floor space must be 36″ min. wide. The width was less than 36″
Thursday, September 1st, 2022
Part 2
We have been discussing when we should make our clear floor space centered on the elements. This is a continuation of the commercial guidelines outlined in the ADA. For Part 1 refer to the
August Newsletter.Below are some other instances that the ADA will require that there be a clear floor space that is centered.
Residential Kichen Work Surface
In kitchens of residential dwelling units (not located in multi-family housing, but required by section 233 to be accessible, there is a requirement to provide a “work surface” with a knee clearance with a floor space centered and allowing a forward approach.
804.3 Kitchen Work Surface (Residential only)
804.3.1 Clear Floor or Ground Space. A clear floor space complying with 305 positioned for a forward approach shall be provided. The clear floor or ground space shall be centered on the kitchen work surface and shall provide knee and toe clearance complying with 306.
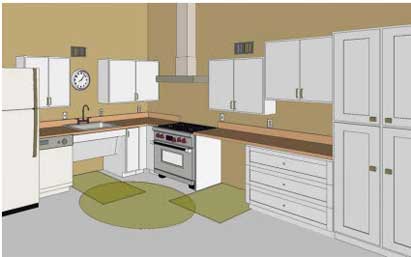
The image above shows a residential kitchen with a sink as well as a “work surface” which provides a forward approach. The work surface is required that the clear floor space below it be centered at the surface. The sink is not required to provide a clear floor space that is centered.

The image above shows a residential kitchen work surface and it is centered at the surface.
Altered Sales and Service counter
When an existing sales and service counter is altered, they must provide an accessible portion. Typically a sales or service counter must be 36″ long minimum, but if they cannot accommodate that length they would be allowed to only provide a 24″ counter as long as there is a clear lfoor space centered and parallel to the counter.
904 Sales and Service counters
904.4 Sales and Service Counters.
EXCEPTION: In alterations, when the provision of a counter complying with 904.4 would result in a reduction of the number of existing counters at work stations or a reduction of the number of existing mail boxes, the counter shall be permitted to have a portion which is 24 inches (610 mm) long minimum complying with 904.4.1 provided that the required clear floor or ground space is centered on the accessible length of the counter.
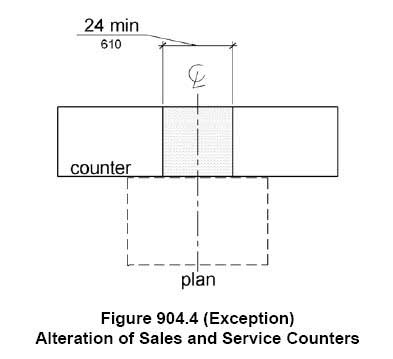

The image above shows an example of a counter which has a parallel approach at the lower counter and the clear floor space is also centered at the accessible portion. The length is unknown, but this would be an example of how the exception could be taken.
Playground transfer system
When playgrounds have elevated components that require an accessible route, one way that they can reach the elevated portion is via a transfer system. That transfer system will also require to have a parallel clear floor space centered at the platform.
1008.3Playground Transfer Systems
1008.3.1.3 Transfer Space. A transfer space complying with 305.2 and 305.3 shall be provided adjacent to the transfer platform. The 48 inch (1220 mm) long minimum dimension of the transfer space shall be centered on and parallel to the 24 inch (610 mm) long minimum side of the transfer platform. The side of the transfer platform serving the transfer space shall be unobstructed.
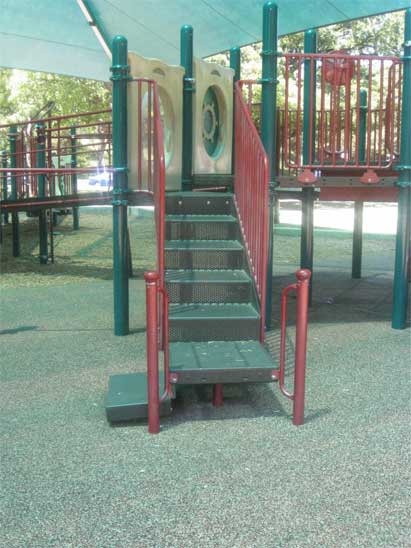
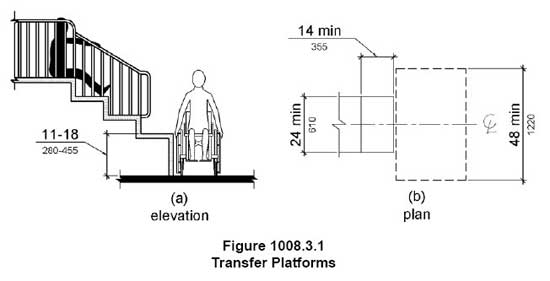

The image above shows a transfer system at an elevated play structure. There is room for the clear floor space to be centered at the platform.
Pool transfer walls and platforms
Pools and spas (jacuzzis/hot tubs) are required to have an accessible entry (or two depending on the size of the pool). There are several options for the accessible entry. One is a transfer wall and another a transfer platform. The transfer wall or the transfer platform must have a clear floor space centered at the deck to assist with entry to the pool.
1009.4 Pool Transfer Walls
1009.4.1 Clear Deck Space. A clear deck space of 60 inches (1525 mm) minimum by 60 inches (1525 mm) minimum with a slope not steeper than 1:48 shall be provided at the base of the transfer wall. Where one grab bar is provided, the clear deck space shall be centered on the grab bar. Where two grab bars are provided, the clear deck space shall be centered on the clearance between the grab bars.
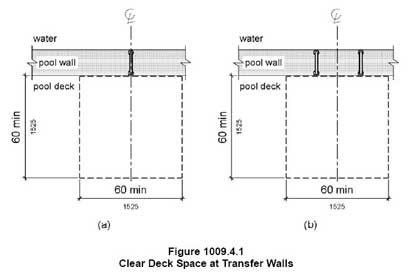

The image above shows a transfer wall with two grab bars at a jacuzzi. There is room for the clear floor space to be centered between the two grab bars.
1009.5 Pool Transfer Platform
1009.5.2 Transfer Space. A transfer space of 60 inches (1525 mm) minimum by 60 inches (1525 mm) minimum with a slope not steeper than 1:48 shall be provided at the base of the transfer platform surface and shall be centered along a 24 inch (610 mm) minimum side of the transfer platform. The side of the transfer platform serving the transfer space shall be unobstructed.
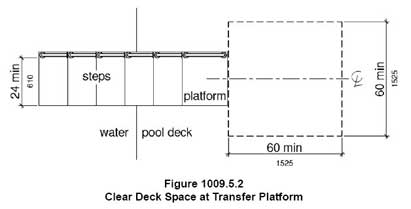

1) Texas Association of Interior Design
Ludowici Dallas Design Center | 133 Manufacturing St, Dallas, TX 75207
Monday, August 1st, 2022
Part 1
In the 2010 ADA and the 2012 Texas Accessibility Standards there are certain elements that require front approach and centered clear floor space on the element, but not all of them do. This newsletter will enumerate the one’s that do. Other elements such as lavatories and sinks only require forward approach but the clear floor space is not required to be centered.
Below are the elements that require a clear floor space to be centered:
Drinking fountains
Drinking fountains are one of the elements listed in the ADA and TAS that require that the wheelchair drinking fountain have a clear floor space centered on the unit. The clear floor space must also be a forward approach.
602 Drinking Fountains
602.2 Clear Floor Space. Units shall have a clear floor or ground space complying with 305 positioned for a forward approach and centered on the unit. Knee and toe clearance complying with 306 shall be provided
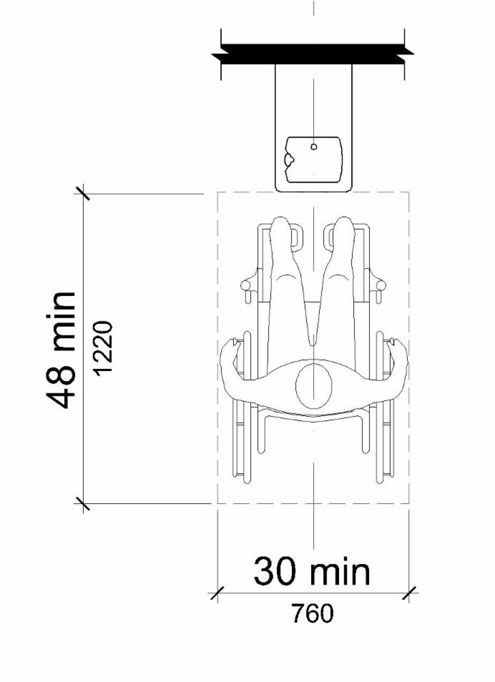
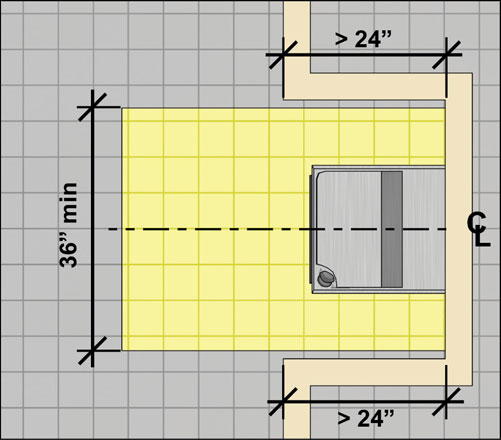
The image above shows the required clear floor space at the drinking fountain. It must be a forward approach and it must be centered on the wheelchair accessible drinking fountain. If it is located at an alcove deeper than 24″ the clear floor space must be widened to 36″ wide.
There are two violations that occurr with this requirement. One is that sometimes the drinking fountains are located along a corridor and not in an alcove. This creates a protruding object issues (see this newsletter that explains that). In order to resolve the protruding object, a cane dectable apron is sometimes installed at the bottom of the “high” drinking fountain and the apron reduceds the ability to have a forward approach because it might be lower than 27″ a.f.f.
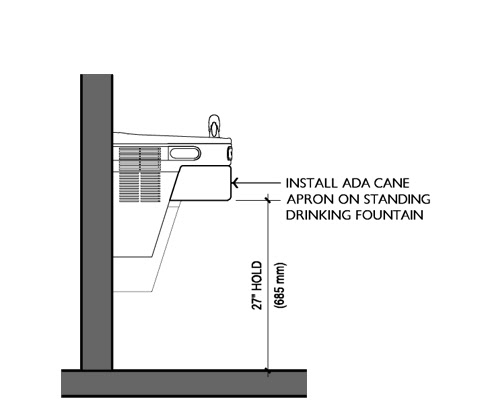
The image above shows how the clear floor space centered under the “low” drinking fountain spans below the “high” one and if there is an apron below the 27″ a.f.f. it will prevent the use of the drinking fountain by a wheelchair.
Number two is that sometimes the drinking fountains are located in an alcove and the walls creating the alcove reduce the 30″ clearance which must be centered. The wall adjacent to the wheelchair accessible drinking fountain should be a minimum distance of 15″ from the centerline of the drinking fountain to the inside of the wall.
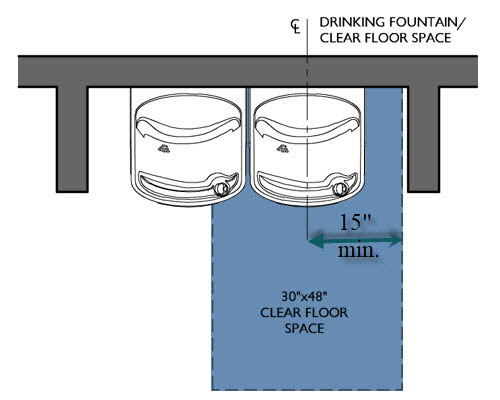
The image above shows how the clear floor space centered under the “low” drinking fountain must be a minimum of 15″ from the center of the drinking fountain to the inner edge of the alcove.
Washer and Dryer
The washer and dryer must also have the clear floor space centered on the appliance and must have parallel approach.
611 Washer and Dryer
611.2 Clear Floor Space. A clear floor or ground space complying with 305 positioned for parallel approach shall be provided. The clear floor or ground space shall be centered on the appliance.
This sometimes causes issues if the washer and dryer are located inside a closet. The doors may reduce the clearance.
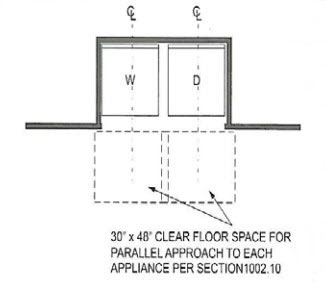

The image above shows a set of washer and dryer located inside a utility closet. The doors do not open 180 degrees and reduce the clear floor space to less than 24″ from the centerline of the dryer to the edge of the floor space.
Signage
The signage that designate permanent rooms must have an 18″x18″ clear floor space centered on the sign.
703 Signage
703.4.2 Location. ….Signs containing tactile characters shall be located so that a clear floor space of 18 inches (455 mm) minimum by 18 inches (455 mm) minimum, centered on the tactile characters, is provided beyond the arc of any door swing between the closed position and 45 degree open position.

The image above shows a sign which has a drinking fountain in front of it, therefore the requirement for a clear floor space centered on the sign has not been met.
Lavatories and Sinks
One of the misconceptions is that a clear floor space at the sink or lavatory is required to be centered. The approach must be forward, but the clear floor space is not noted as needing to be centered, like the other sections do. Therefore by omission we understand that the clear floor space can be offset.
606 Lavatories and Sinks
606.2 Clear Floor Space. A clear floor space complying with 305, positioned for a forward approach, and knee and toe clearance complying with 306 shall be provided.
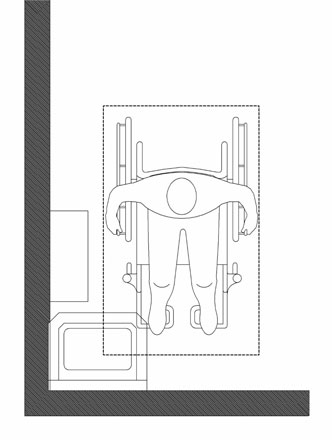
The image above shows a wheelchair clear floor space that is not centered at the lavatory. The clear floor space under the lavatory can be offset if there is an obstruction such as a paper towel dispenser next to the lavatory.
Wednesday, June 1st, 2022
Introduction:
Accessible signage can be a very confusing topic. Even after all these years of practicing my accessibility consulting, I am still learning a thing or two. Sadly they can even be confusing to signage manufacturers and installers.
Accessible signs require the following things:
- Raised and Brailled Characters
- Contrasting background
- San Serif Fonts
- If using Pictogram, there are requirements
- If depicting accessible spaces the use of the ISA (International Symbol of Access)
This newsletter will focus on a few common errors I encounter during my inspections.
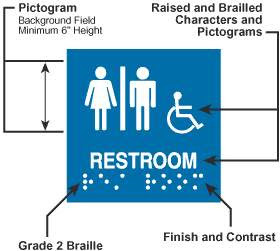
Raised Characters
The accessible signage will require that the characters describing the space whether it be a number or letters, must be raised. They should be at least 1/32″ above the surface of the sign.
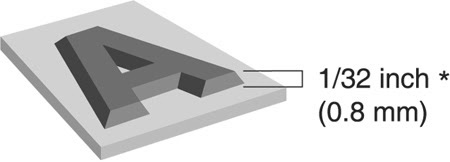
This graphic shows the minimum requirement for the raised characters of a sign.
There should also be Braille below the words that states the same words that are provided. So all words and numbers should be duplicated by Braille

The restroom had a painted sign on the door but the characters were not raised and it did not have brailled as a duplicate. This is not compliant

The restroom sign has both raised letters and characters and braille duplicated below the words. This is a compliant sign..
Pictograms
What are pictograms? It is a figure that represents the words of the sign. Pictograms are not required, but if you use them the field they are in should be 6″ minimum. The pictogram can be smaller than that, but the field must be at least 6″ tall.
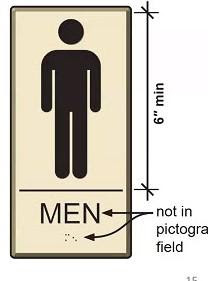
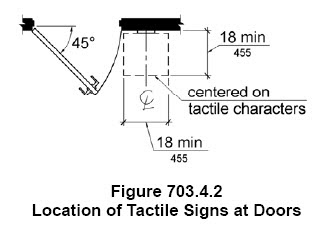
Pictograms must be located ABOVE the words they are describing. Per section 703
703.6.3 Text Descriptors. Pictograms shall have text descriptors located directly below the pictogram field. Text descriptors shall comply with 703.2, 703.3 and 703.4.

The pictogram at this sign is located below the words describing it. That is not compliant
Monday, May 2nd, 2022
Introduction:
Changes to the Texas Accessiblity Standards have been proposed and are open for public comments. The new standard, once adopted would be called The 2022 Texas Accessibility Standards.
This newsletter will give you a few proposed changes. These have not been adopted yet, and if you have any comments for TDLR before they implement them, the comments will be accepted until May 9th, 2022 using this link
2022 Texas Accessibility Standards Changes
Here are a few of the changes that are being proposed:
1. Outdoor Developed Areas. There will be a brand new chapter for Outdoor developed areas, Section 245 and Chapter 11. These will include trails, beaches, camping and picnic areas (just to name a few).
2. Advisory. Many of the advisories have become part of the Standards
3. Definition of Alteration. The definition of “alteration” has change slightly to include clarification on “circulation paths”. It now includes flooring as part of the definition:
106.5.5 Alteration. A change to a building or facility that affects or could may affect the usability of the building or facility or portion thereof. Alterations include, but are not limited to, remodeling, renovation, rehabilitation, reconstruction, historic restoration, resurfacing of circulation paths or vehicular ways including carpets, floors, or fields, changes or rearrangement of the structural parts or elements, and changes or rearrangement in the plan configuration of walls and full-height partitions.
Normal maintenance, reroofing, painting or wallpapering, or changes to mechanical and electrical systems are not alterations unless they affect the usability of the building or facility
The exemption for employee work areas clarified what “approach, enter and exit” means
203.9 Employee Work Areas. …..
“Approach, enter, and exit” means that people using wheelchairs must be able to enter and back out of the space. Employee work area doors, doorways, and gates, therefore, must comply with TAS 404 except the maneuvering clearance is limited to the “enter” side unless required for egress by TAS 207.1.
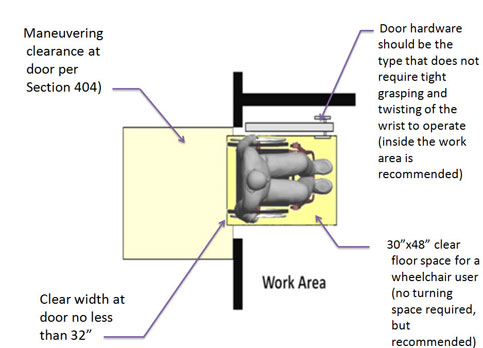
The picture above shows the diagram which explains the requirements for a work area entrance.
4. Licensed Physical and Occupational Therapy spacesused to have to go through a variance process in order to allow them not to be accessible. The proposed changes makes them not required and will no longer need a variance.
203.15 Licensed Physical and Occupational Therapy Training Areas Including Bathrooms and Kitchens. Licensed provider areas that are purposefully inaccessible for the intent of training persons with disabilities to function in a simulated home environment for when they leave therapy and return home shall not be required to comply with accessible features. The user must be able to get to the area but may not necessarily be required to provide an accessible route within the space for training purposes.

Physical Therapy areas will no longer require a variance not to comply
5. Electrical Vehicle Charging Stations. TDLR has issued many Technical Memos throughout the years. The 2022 TAS will incorporate some as part of the standards. One of them is about Electrical Vehicle parking and charging spaces. The requirements will now be part of the 2022 TAS in section 244, 208 and 502.
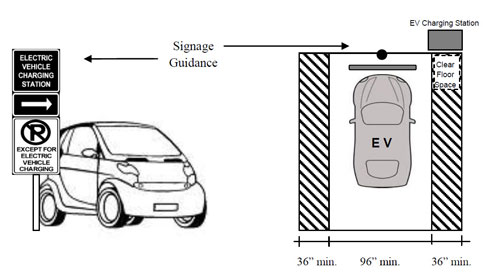
This is the requirements from the Technical Memo for Electrical Vehicle Charging Stations. They will now be part of the new standards
 .
.
A built example

A charging station. The 2022 TAS will require a clear floor space to reach the accessible one.
6. 208.1 Parking Facilties. TDLR has clarified that parking facilities that are served by valet parking are not exempted from compliance with 208 and must have accessible parking.
7. Curb ramps at public right of way. THEY’RE BACK!!! Detectable warnings (truncated domes with contrasting color) are being proposed to come back on the Standards. Don’t kill me!

curb ramps located within the public right of way are proposed to have detectable warnings.
Be sure you get involved in the public comments. We need your voices and opinions to be heard to ensure that the Standards are clear and are providing proper guidance for design professionals so we can design and build environments for persons with disabilities that are inclusive and safe.
Friday, April 1st, 2022
Introduction:
If you have been around for a minute in the building industry you have seen our esteemed “truncated domes” come and go, and come and go…well it happened again….When the ADAAG was published in 1991, there was a section called “Detectable Warnings”. These were elements used for people that were visually impaired to assist them in navigating their exterior environment. A detectable warning had texture and contrasting color so a person who used a cane could feel the texture as he walked and maybe if they had low vision they could detect a change in color. Both of these methods allowed them to be aware that there might be a hazard on its way.
The detectable warning texture was required to be “truncated domes” located at a curb ramp and later it was added to pedges at a train track platforms.
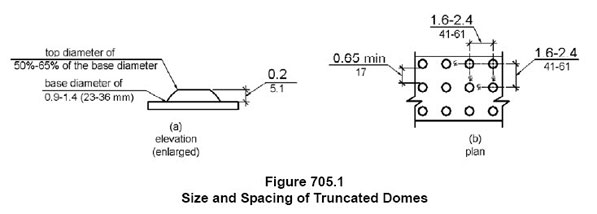

This is a curb ramp inside the property line with detectable warnings.
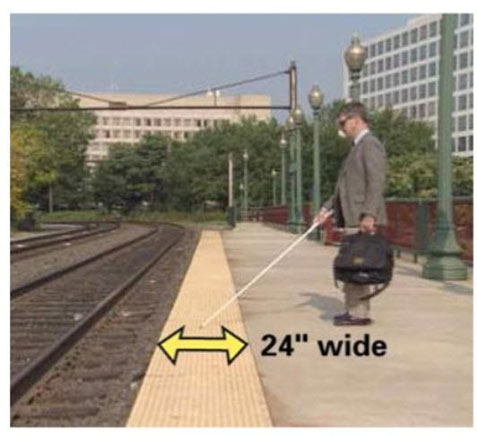

This is a train platform edge with detectable warnings.
The ADA Standards for Accessible Design and the Texas Accessibility Standards
After the 2010 ADA Standards for Accessible Design was passed into law, the rules about detectable warnings changed. Before, detectable warnings were required at curb ramps. The new version now only requires it at train platform edges. Curb ramps inside of the property line (which is all that ADA regulates) will no longer require texture or color on it.

The picture above built in microwaves mounted above the 48″ allowable reach range. They added a counter top microwave that was not built in. This does not alleviate the lack of reach range.
Public Right of Way
The Public Right of Way guidelines (which are only proposed and have not been adopted), as well as municipalities and Department of Transportation may require that detectable warnings be provided at the bottom 24″ of the curb ramp. This will allow people that are visually impaired be aware that there might be a hazard beyond the texture.
The ADA does not have requirements beyond the property line. Therefore the public right of way does not fall under the ADA.
The Texas Department of Licensing and Regulation used to have a section in Chapter 68 which required detectable warnings at curb ramps within the public right of way, but they eliminated that in the most current version of the Rules. Click Here to see what they require.
TDLR no longer requires detectable warning at curb ramps at the public right of way.
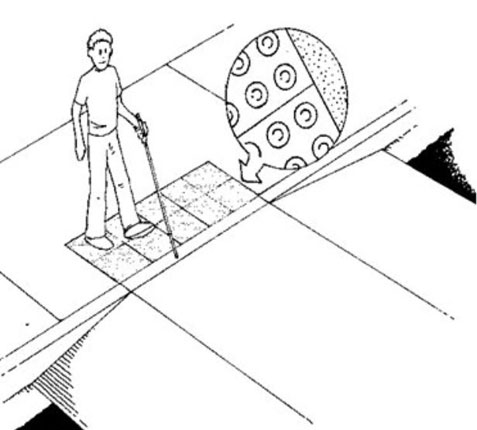
The figure above shows the requirement for detectable warnings listed in the Public Right of Way Guidelines

The curb ramp has detectable warnings per the Department of Transportation and the Public Right of Way Guidelines. Check your municipality to make sure what it requires
Tuesday, March 1st, 2022
Introduction:
I perform ADA, Fair Housing and Texas Accessibility Standards on site inspection and assessments every Wednesday. Some days I find unique conditions that I like to share with you so we can learn from them and be sure they do not happen to you also. This newsletter will give you some of my latest intersting finds.
Vision Lights at Doors
The ADA requires that all doors that require user passage comply with all the portions of the section 404. Door that reqired “user passage”
But are all doors required to comply? What about doors that are only used for employees? The doors shown below are into a commercial kitchen. The vision lights for doors that allow user passage must be mounted no higher than 43″ a.f.f., but these type of doors have the vision light mounted higher. Here is the standard:
404.2.11 Vision Lights. Doors, gates, and side lights adjacent to doors or gates, containing one or more glazing panels that permit viewing through the panels shall have the bottom of at least one glazed panel located 43 inches (1090 mm) maximum above the finish floor.
The vision lights requirement are for ALL doors that require user passage unless the room beyond is excempted (like IT closets or other machinery spaces). Employee work area doors must have the ability to approach, enter and exit, therefore those doors into employee work areas like commercial kitchens will also have to comply.
During one of my inspections, I went to a restaurant and they had the door into the kitchen with vision lights higher than 43″ a.f.f. The owner was confused. It is not so simple to understand why this door would have to comply, but keep in mind that the ADA protects persons with disabilities from discrimination at the work place. If a person in a wheelchair gets hired as manager, the vision light allows them to see inside so they don’t get hit by the door. Be sure to specify one of the doors with the vision lights lower.


The picture above shows a commercial kitchen door with vision lights mounted higher than 43″ a.f.f. This is not compliant.
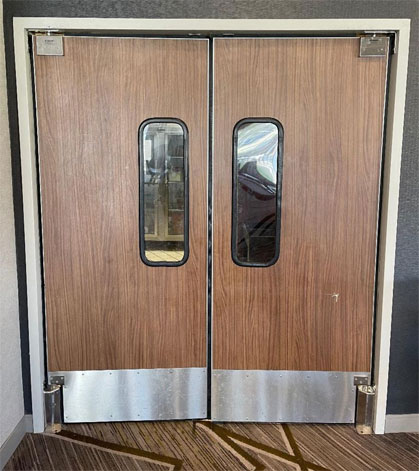


The picture above shows a commercial kitchen door with vision lights mounted lower than 43″ a.f.f. This is compliant.
Fixed or Built in elements
The ADA only deals with fixed or built in elements. At one of my inspections there was a break room with built in microwaves that were mounted higher than the allowable reach range. To solve the violation they added a microwave to the counter. This did not resolve the violation, because it is not a “built in” element and does not satisfy the requirement. Below is what the ADA states about what elements are scoped in the standards:
“Scope of coverage. The 1991 Standards and the 2010 Standards apply to fixed or built-in elements of buildings, structures, site improvements, and pedestrian routes or vehicular ways located on a site. Unless specifically stated otherwise, the advisory notes, appendix notes, and figures contained in the 1991 Standards and the 2010 Standards explain or illustrate the requirements of the rule; they do not establish enforceable requirements.”

The picture above built in microwaves mounted above the 48″ allowable reach range. They added a counter top microwave that was not built in. This does not alleviate the lack of reach range.
Protruding Objects
There are rules in the ADA Standards that pertain to people who are visually impaired. Since they cannot detect objects mounted higher than 27″ a.f.f. we typically design and built the objects so that they are recessed or have some sort of cane detection. But in one of my inspections, the drinking fountain was recessed, but not far enough, so that the leading edge was still projecting onto the circulation path more than 4″

The picture above shows a recessed drinking fountain that is located in a corridor. But the leading edge still projects more than 4″ onto the circulation path and therefore was considered a violation of the protruding object rule

The drinking fountain projects 5″ ontothe circulation path














 Abadi
Abadi 































 .
.






























 .
.













